Ids 007 trojan horse
0 likes79 views
Trojans are malware that disguise themselves to gain access to a user's computer without their awareness. They spread by tricking users into downloading email attachments or clicking on fake advertisements. Once installed, they can allow hackers to access personal information, delete files, or use the computer as an anonymizing proxy for illegal activities. Examples include Zeus, which steals banking credentials, and CryptoLocker ransomware, which encrypts files until a ransom is paid. Trojans demonstrate that no system is immune, as shown by the Mac Flashback Trojan.
1 of 16
Download to read offline











Ad
Recommended
Ids 006 computer worms
Ids 006 computer wormsjyoti_lakhani A computer worm is a standalone malware program that replicates itself and spreads to other computers by exploiting security vulnerabilities. It uses network resources to scan for vulnerable systems and transfer itself, potentially infecting many computers and overloading networks. Notable examples of worms include Morris worm, which disrupted computers on the early Internet in 1988, and Conficker, which infected over 9 million systems worldwide in 2008. Worms are generally more infectious than viruses due to their ability to spread autonomously across networks.
Internet Security
Internet SecurityManoj Sahu This document provides information about viruses, worms, and Trojans, including their definitions, histories, and how to prevent attacks. Viruses copy themselves and travel to other programs/files to spread, while worms are self-contained programs that can spread functional copies of themselves across networks. Trojans masquerade as useful software but cause damage once installed. Examples of recent major viruses, worms, and Trojans throughout history are also outlined, along with their harmful effects and methods of detection and prevention. The key differences between viruses, worms, and Trojans are also summarized.
5 worms and other malware
5 worms and other malwaredrewz lin Worms spread rapidly across networks by exploiting software vulnerabilities. The Morris Worm in 1988 infected 6000 computers in hours by exploiting vulnerabilities in sendmail and fingerd. Later worms like Code Red, Nimda, and Blaster also spread quickly and caused outages by attacking Microsoft software. Malware continues to be a threat and includes rootkits, botnets, spyware, and more.
Cybercrime: Virus and Defense
Cybercrime: Virus and DefenseMd.Tanvir Ul Haque The document discusses cybercrime, particularly focusing on viruses as a form of malicious software. It outlines the types, properties, life cycles of viruses, notable historical milestones in virus development, and prevention methods against infections. Various types of viruses, including boot sector, file infecting, macro, metamorphic, polymorphic, and multipartite viruses are also described.
Computer Virus
Computer Virusizzul Computer viruses are programs that spread from one computer to another without permission. They can corrupt or delete files, use email to spread, or erase entire hard disks. Viruses are often spread through email attachments, downloads, or infected files on networks. While some only replicate, others can damage computers. It is important to have antivirus software and be cautious of suspicious files from untrusted sources. Different types of malware include viruses, worms, trojans, and bacteria, each with their own methods of spreading and behaviors.
Computer virus
Computer virusRohit Nayak Computer viruses can infect computers through infected floppy disks or programs. There are two main types: file viruses, which infect executable files, and boot sector viruses, which infect the boot sector of disks. Viruses spread by replicating themselves and transferring to other disks or files. They can damage systems by corrupting or deleting files and programs. Users can prevent viruses by avoiding untrusted disks and files, updating antivirus software, and being wary of email attachments. Once infected, antivirus software must be used to detect and remove the virus.
Computer virus (Microsoft Word)
Computer virus (Microsoft Word)ainizbahari97 This document provides information about computer viruses including what they are, how they spread, and how to remove them. It defines viruses as small programs that can copy themselves and infect computers without permission in order to interfere with operations. Viruses are often spread through email attachments and downloading files. To remove a virus, the document recommends using an online scanner from Microsoft or another security provider and checking for antivirus software updates. It also provides examples of other types of malware like worms, trojans, and bacteria that differ from viruses in their behaviors.
Presentation on virus
Presentation on virusProtik Roy The document provides a comprehensive overview of computer viruses, detailing their definition, history, types, and examples. It explains the phases of virus activity, symptoms of infection, and the distinctions between viruses, worms, trojans, phishing sites, and spyware. The document emphasizes the importance of combating viruses with anti-virus software and firewalls.
Internet worm-case-study
Internet worm-case-studyIan Sommerville In November 1988, a student at Cornell University deliberately released a program called the Internet Worm that exploited security vulnerabilities in Unix systems and spread across computers connected to the Internet. The worm did not cause direct damage but its replication overloaded systems and severely disrupted network services. It took system administrators several days to devise and implement modifications to vulnerable programs to stop the spread of the worm and clear infected machines. This was the first widely distributed Internet security threat and highlighted the importance of securing systems and patching vulnerabilities.
computer vipin kumar ppt
computer vipin kumar pptvipinkumar940 Computer viruses, worms, and Trojan horses pose a threat to computers. Viruses spread from file to file on a computer but require file sharing to infect other computers. Worms exploit networks to spread rapidly from computer to computer. Trojan horses appear harmless but damage or steal information from infected computers. While most viruses and worms only self-replicate, some are programmed to damage systems through payloads like deleting files. Virus writers aim to evade detection through techniques like polymorphism that mutate code to avoid consistent fingerprints.
Trojan horse
Trojan horseGaurang Rathod This document discusses Trojan horse malware, including its definition, objectives, types, techniques, and methods of implementation and prevention. It defines a Trojan horse as malware that appears harmless but performs malicious functions. It provides examples of how Trojans can be used to gain unauthorized access to systems and describes common types. The document also gives an example of how a keylogger Trojan could be implemented to steal banking passwords and outlines various prevention strategies like antivirus software, firewalls, and education.
Virus
VirusProtik Roy This document provides an outline for a presentation on computer viruses. It defines viruses and discusses their naming, types, examples, infection phases, and symptoms. It focuses specifically on Trojans, phishing sites, combating viruses with anti-viruses and firewalls, and safe computing practices. The outline covers virus history, definitions, major examples, and details on file, boot sector, macro, and multipartite viruses. It also explains symptoms of infection and strategies for prevention and recovery.
virus,worms & analysis
virus,worms & analysisPriyatham Galisetty This document provides an overview of viruses, worms, trojans and spyware. It discusses the differences between these types of malware and their modes of transmission. The document then describes the life cycle of a virus, including the infection and attack phases. It outlines some common indications that a system may be infected with a virus. Finally, it discusses some methods that viruses use to avoid detection by antivirus software, such as killing antivirus tasks, self-modification, and encryption with variable keys.
Virus vs anti virus
Virus vs anti virusXʎz ʞsɥ Computer viruses are malicious software programs that can damage computers. They replicate and spread by infecting files. Different types of viruses exist, including memory resident viruses that hide in RAM, direct action viruses that infect files specified in AUTOEXEC.BAT, and boot sector viruses that infect the boot sector of hard disks. Anti-virus software detects, prevents, and removes viruses to protect computers and personal information from being damaged, stolen, or misused by viruses. Having anti-virus software installed provides various advantages like preventing viruses from formatting disks, deleting files, and slowing down computers.
Computer virus
Computer virusDark Side The document is a seminar report on computer viruses submitted for a B.Tech degree, highlighting the definition, types, and impacts of computer viruses. It discusses various virus categories, including worms, trojans, adware, rootkits, and ransomware, explaining their behaviors, spread mechanisms, and potential harm. Additionally, it includes acknowledgments, an abstract, and references, alongside figures and tables related to the topic.
Computer Worms
Computer Wormssadique_ghitm This document discusses computer worms, including how they work, types of worms, and examples of major worms. It defines worms as programs that replicate themselves across a network by exploiting security vulnerabilities. The document covers worm target discovery, propagation, activation methods, payloads, examples like Morris worm, Code Red, Nimda, SQL Slammer, and Sobig.f, as well as prevention techniques and current research focus areas.
Computer virus & its cure
Computer virus & its cureTamim Ahmed This document provides an overview of computer viruses and methods for prevention and removal. It defines what a computer virus is and describes different types including boot sector viruses, file infector viruses, worms, macro viruses, and Trojan horses. Examples like Melissa and I Love You are given. Methods for manually removing some common viruses like New Folder.exe and Autorun.inf are outlined. The document stresses the importance of using antivirus software, regularly updating definitions, avoiding unsafe downloads and attachments, and making backups to help prevent and cure computer viruses.
Computer viruses by joy chakraborty
Computer viruses by joy chakrabortyJoy Chakraborty This document discusses information security and privacy issues related to computer viruses. It begins by providing background on viruses and their ability to cause damage and disruption. It then defines what a computer virus is and describes how they work, infecting other programs and replicating. The document outlines various ways viruses can be acquired and categories of viruses. It also discusses the lifecycle of viruses and measures that can be taken to prevent virus infections, including using antivirus software and firewalls. The document concludes by covering data security issues, common types of security breaches, and the costs to companies from virus damage.
Computer virus
Computer virusManjula Pradeep Gunathilake Computer viruses are malicious software programs that can damage computers and spread without permission. Viruses are often transmitted by email attachments, downloaded files, removable drives, and through networks. They work by attaching themselves to other programs or files. To prevent virus infections, it is important to have up-to-date antivirus software installed and configured to run regularly, only open trusted email attachments, be careful when downloading files, and back up files frequently.
Computer virus
Computer virusRahul Baghla This document provides information about computer viruses presented by a student group. It defines a computer virus, describes common types of viruses like Trojans and worms, and explains how viruses infect systems. The document also outlines signs of a virus attack, how to create a virus for educational purposes only, and methods for protecting against and removing viruses like installing antivirus software and deleting suspicious files. The presentation aims to educate users about computer viruses and promoting safe computing practices.
Computer Virus
Computer VirusAritra Das A computer virus is a program that disrupts normal computer operations by infecting and destroying data and entering computers without user permission or knowledge. Viruses self-replicate by infecting more files, slowing computers down and destroying data. They enter via infected floppy disks or the internet/email. Viruses remain inactive until triggered to harm data and programs. Antivirus software identifies, prevents, and removes viruses by scanning files against known virus definitions and suspicious program behaviors.
Presentation Slide: Computer Virus
Presentation Slide: Computer VirusYo Maruf A presentation on computer viruses was given by Farid uddin bhuiyan. The presentation defined a computer virus as a program that damages computer systems and destroys or erases data files. It described seven common types of computer viruses and explained how viruses work by exploiting vulnerabilities on interconnected systems. Signs of a virus infection were provided, such as unusual screen messages or slowed computer performance. The presentation concluded by recommending ways to prevent virus infections, such as keeping anti-virus software updated weekly and backing up important files.
Computer Virus
Computer VirusRajah Anuragavan This document discusses computer viruses, including what they are, the types of viruses, and how to prevent and remove them. It defines a computer virus as a program that can copy itself and infect other applications and files. The main types are boot sector viruses, which infect boot drives; program viruses, which infect executable files; and multipartite viruses, which combine the two. The document also lists some of the top sources of virus attacks and recommends using antivirus software like Norton, McAfee, and Kaspersky to scan for and remove viruses, as well as maintaining regular updates and safe digital practices.
Computer viruses
Computer virusesImran Khan This document provides an overview of the history, classifications, and structure of computer viruses. It discusses how viruses can replicate and spread from one computer to another by modifying other programs to include a copy of themselves. Viruses are typically 200-4000 bytes and are classified based on their structure and infection method, such as shell, add-on, and intrusive viruses. The document also outlines the key components of viruses, including search, copy, anti-detection, and payload. It describes the evolution of viruses from early generations that were simple and easy to detect to more advanced generations that are stealthy, armored, and polymorphic.
presentation on computer virus
presentation on computer virusYogesh Singh Rawat This document discusses computer viruses including their similarities to biological viruses, how they work and spread, types of viruses, virus detection methods, and prevention. It notes that computer viruses can replicate and spread like biological viruses, infecting host systems and slowing them down. The main types discussed are macro, boot sector, worm, Trojan horse, and logic bomb viruses. Virus detection methods covered include signature-based, behavior-based, and heuristic-based detection. Prevention methods recommended are using antivirus software, not sharing drives without passwords, deleting email attachments, backing up files, and using secure operating systems.
Virus soran university
Virus soran universityRebaz Hamad The document provides an overview of computer viruses, detailing various types such as boot sector viruses, file infector viruses, and Trojan horses, along with their methods of operation. It explains how viruses replicate and damage data, and describes the operation of antivirus software in detecting and neutralizing these threats. The authors are Harem Abdullstar, Rebaz Abdullqadr, and Omer Muhammed, supervised by Mr. Aras Masoud.
Trojan horse nitish nagar
Trojan horse nitish nagarNitish Nagar A Trojan horse is a type of malware that masquerades as legitimate software to trick users into installing it. It can then perform harmful actions like stealing personal information, corrupting files, or installing additional malware. Trojans are spread through attachments, downloads from untrusted websites, and instant messages. Common goals of attackers are to steal credit cards, passwords, work files, or install backdoors on infected systems. Users should be wary of unsolicited files from untrusted sources.
Malware- Types, Detection and Future
Malware- Types, Detection and Futurekaranwayne The document provides an overview of malware, including its definition, types (like viruses, worms, and trojans), historical malware examples, and detection methods. It discusses notable malware incidents such as the Morris Worm, Code Red, and SQL Slammer, and highlights future trends in malware like polymorphic and metamorphic viruses. Methods for malware detection include signature detection, change detection, and anomaly detection, each with their advantages and limitations.
Torjan horse virus
Torjan horse virussumitra22 This document discusses Trojan horses, including their purpose and usage. Common Trojans like Netbus and Subseven are mentioned. The document notes that Trojans do not replicate like viruses but instead facilitate unauthorized access. They can be used to hack into targeted systems and perform actions like using the machine as a botnet node or stealing data and passwords. Recent Trojans take advantage of security flaws in browsers. While antivirus software can help detect some Trojans, they remain a persistent threat, and proper computer security practices are important to prevent infection.
trojon horse Seminar report
trojon horse Seminar reportNamanKikani This document is a seminar report on Trojan horse malware presented by a student named Naman Kikani. It contains an introduction to malware and Trojans, chapters on what Trojans are and how they work, common types of Trojan malware, how Trojans are used, and how to protect yourself from Trojans. The report provides information on how Trojans can give attackers remote access and control over an infected computer without the user's knowledge to steal data or carry out other malicious activities. It describes some specific Trojans like backdoor and ransomware Trojans and explains how programs like Back Orifice work using a client-server model to control an infected machine remotely.
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Internet worm-case-study
Internet worm-case-studyIan Sommerville In November 1988, a student at Cornell University deliberately released a program called the Internet Worm that exploited security vulnerabilities in Unix systems and spread across computers connected to the Internet. The worm did not cause direct damage but its replication overloaded systems and severely disrupted network services. It took system administrators several days to devise and implement modifications to vulnerable programs to stop the spread of the worm and clear infected machines. This was the first widely distributed Internet security threat and highlighted the importance of securing systems and patching vulnerabilities.
computer vipin kumar ppt
computer vipin kumar pptvipinkumar940 Computer viruses, worms, and Trojan horses pose a threat to computers. Viruses spread from file to file on a computer but require file sharing to infect other computers. Worms exploit networks to spread rapidly from computer to computer. Trojan horses appear harmless but damage or steal information from infected computers. While most viruses and worms only self-replicate, some are programmed to damage systems through payloads like deleting files. Virus writers aim to evade detection through techniques like polymorphism that mutate code to avoid consistent fingerprints.
Trojan horse
Trojan horseGaurang Rathod This document discusses Trojan horse malware, including its definition, objectives, types, techniques, and methods of implementation and prevention. It defines a Trojan horse as malware that appears harmless but performs malicious functions. It provides examples of how Trojans can be used to gain unauthorized access to systems and describes common types. The document also gives an example of how a keylogger Trojan could be implemented to steal banking passwords and outlines various prevention strategies like antivirus software, firewalls, and education.
Virus
VirusProtik Roy This document provides an outline for a presentation on computer viruses. It defines viruses and discusses their naming, types, examples, infection phases, and symptoms. It focuses specifically on Trojans, phishing sites, combating viruses with anti-viruses and firewalls, and safe computing practices. The outline covers virus history, definitions, major examples, and details on file, boot sector, macro, and multipartite viruses. It also explains symptoms of infection and strategies for prevention and recovery.
virus,worms & analysis
virus,worms & analysisPriyatham Galisetty This document provides an overview of viruses, worms, trojans and spyware. It discusses the differences between these types of malware and their modes of transmission. The document then describes the life cycle of a virus, including the infection and attack phases. It outlines some common indications that a system may be infected with a virus. Finally, it discusses some methods that viruses use to avoid detection by antivirus software, such as killing antivirus tasks, self-modification, and encryption with variable keys.
Virus vs anti virus
Virus vs anti virusXʎz ʞsɥ Computer viruses are malicious software programs that can damage computers. They replicate and spread by infecting files. Different types of viruses exist, including memory resident viruses that hide in RAM, direct action viruses that infect files specified in AUTOEXEC.BAT, and boot sector viruses that infect the boot sector of hard disks. Anti-virus software detects, prevents, and removes viruses to protect computers and personal information from being damaged, stolen, or misused by viruses. Having anti-virus software installed provides various advantages like preventing viruses from formatting disks, deleting files, and slowing down computers.
Computer virus
Computer virusDark Side The document is a seminar report on computer viruses submitted for a B.Tech degree, highlighting the definition, types, and impacts of computer viruses. It discusses various virus categories, including worms, trojans, adware, rootkits, and ransomware, explaining their behaviors, spread mechanisms, and potential harm. Additionally, it includes acknowledgments, an abstract, and references, alongside figures and tables related to the topic.
Computer Worms
Computer Wormssadique_ghitm This document discusses computer worms, including how they work, types of worms, and examples of major worms. It defines worms as programs that replicate themselves across a network by exploiting security vulnerabilities. The document covers worm target discovery, propagation, activation methods, payloads, examples like Morris worm, Code Red, Nimda, SQL Slammer, and Sobig.f, as well as prevention techniques and current research focus areas.
Computer virus & its cure
Computer virus & its cureTamim Ahmed This document provides an overview of computer viruses and methods for prevention and removal. It defines what a computer virus is and describes different types including boot sector viruses, file infector viruses, worms, macro viruses, and Trojan horses. Examples like Melissa and I Love You are given. Methods for manually removing some common viruses like New Folder.exe and Autorun.inf are outlined. The document stresses the importance of using antivirus software, regularly updating definitions, avoiding unsafe downloads and attachments, and making backups to help prevent and cure computer viruses.
Computer viruses by joy chakraborty
Computer viruses by joy chakrabortyJoy Chakraborty This document discusses information security and privacy issues related to computer viruses. It begins by providing background on viruses and their ability to cause damage and disruption. It then defines what a computer virus is and describes how they work, infecting other programs and replicating. The document outlines various ways viruses can be acquired and categories of viruses. It also discusses the lifecycle of viruses and measures that can be taken to prevent virus infections, including using antivirus software and firewalls. The document concludes by covering data security issues, common types of security breaches, and the costs to companies from virus damage.
Computer virus
Computer virusManjula Pradeep Gunathilake Computer viruses are malicious software programs that can damage computers and spread without permission. Viruses are often transmitted by email attachments, downloaded files, removable drives, and through networks. They work by attaching themselves to other programs or files. To prevent virus infections, it is important to have up-to-date antivirus software installed and configured to run regularly, only open trusted email attachments, be careful when downloading files, and back up files frequently.
Computer virus
Computer virusRahul Baghla This document provides information about computer viruses presented by a student group. It defines a computer virus, describes common types of viruses like Trojans and worms, and explains how viruses infect systems. The document also outlines signs of a virus attack, how to create a virus for educational purposes only, and methods for protecting against and removing viruses like installing antivirus software and deleting suspicious files. The presentation aims to educate users about computer viruses and promoting safe computing practices.
Computer Virus
Computer VirusAritra Das A computer virus is a program that disrupts normal computer operations by infecting and destroying data and entering computers without user permission or knowledge. Viruses self-replicate by infecting more files, slowing computers down and destroying data. They enter via infected floppy disks or the internet/email. Viruses remain inactive until triggered to harm data and programs. Antivirus software identifies, prevents, and removes viruses by scanning files against known virus definitions and suspicious program behaviors.
Presentation Slide: Computer Virus
Presentation Slide: Computer VirusYo Maruf A presentation on computer viruses was given by Farid uddin bhuiyan. The presentation defined a computer virus as a program that damages computer systems and destroys or erases data files. It described seven common types of computer viruses and explained how viruses work by exploiting vulnerabilities on interconnected systems. Signs of a virus infection were provided, such as unusual screen messages or slowed computer performance. The presentation concluded by recommending ways to prevent virus infections, such as keeping anti-virus software updated weekly and backing up important files.
Computer Virus
Computer VirusRajah Anuragavan This document discusses computer viruses, including what they are, the types of viruses, and how to prevent and remove them. It defines a computer virus as a program that can copy itself and infect other applications and files. The main types are boot sector viruses, which infect boot drives; program viruses, which infect executable files; and multipartite viruses, which combine the two. The document also lists some of the top sources of virus attacks and recommends using antivirus software like Norton, McAfee, and Kaspersky to scan for and remove viruses, as well as maintaining regular updates and safe digital practices.
Computer viruses
Computer virusesImran Khan This document provides an overview of the history, classifications, and structure of computer viruses. It discusses how viruses can replicate and spread from one computer to another by modifying other programs to include a copy of themselves. Viruses are typically 200-4000 bytes and are classified based on their structure and infection method, such as shell, add-on, and intrusive viruses. The document also outlines the key components of viruses, including search, copy, anti-detection, and payload. It describes the evolution of viruses from early generations that were simple and easy to detect to more advanced generations that are stealthy, armored, and polymorphic.
presentation on computer virus
presentation on computer virusYogesh Singh Rawat This document discusses computer viruses including their similarities to biological viruses, how they work and spread, types of viruses, virus detection methods, and prevention. It notes that computer viruses can replicate and spread like biological viruses, infecting host systems and slowing them down. The main types discussed are macro, boot sector, worm, Trojan horse, and logic bomb viruses. Virus detection methods covered include signature-based, behavior-based, and heuristic-based detection. Prevention methods recommended are using antivirus software, not sharing drives without passwords, deleting email attachments, backing up files, and using secure operating systems.
Virus soran university
Virus soran universityRebaz Hamad The document provides an overview of computer viruses, detailing various types such as boot sector viruses, file infector viruses, and Trojan horses, along with their methods of operation. It explains how viruses replicate and damage data, and describes the operation of antivirus software in detecting and neutralizing these threats. The authors are Harem Abdullstar, Rebaz Abdullqadr, and Omer Muhammed, supervised by Mr. Aras Masoud.
Trojan horse nitish nagar
Trojan horse nitish nagarNitish Nagar A Trojan horse is a type of malware that masquerades as legitimate software to trick users into installing it. It can then perform harmful actions like stealing personal information, corrupting files, or installing additional malware. Trojans are spread through attachments, downloads from untrusted websites, and instant messages. Common goals of attackers are to steal credit cards, passwords, work files, or install backdoors on infected systems. Users should be wary of unsolicited files from untrusted sources.
Malware- Types, Detection and Future
Malware- Types, Detection and Futurekaranwayne The document provides an overview of malware, including its definition, types (like viruses, worms, and trojans), historical malware examples, and detection methods. It discusses notable malware incidents such as the Morris Worm, Code Red, and SQL Slammer, and highlights future trends in malware like polymorphic and metamorphic viruses. Methods for malware detection include signature detection, change detection, and anomaly detection, each with their advantages and limitations.
Similar to Ids 007 trojan horse (20)
Torjan horse virus
Torjan horse virussumitra22 This document discusses Trojan horses, including their purpose and usage. Common Trojans like Netbus and Subseven are mentioned. The document notes that Trojans do not replicate like viruses but instead facilitate unauthorized access. They can be used to hack into targeted systems and perform actions like using the machine as a botnet node or stealing data and passwords. Recent Trojans take advantage of security flaws in browsers. While antivirus software can help detect some Trojans, they remain a persistent threat, and proper computer security practices are important to prevent infection.
trojon horse Seminar report
trojon horse Seminar reportNamanKikani This document is a seminar report on Trojan horse malware presented by a student named Naman Kikani. It contains an introduction to malware and Trojans, chapters on what Trojans are and how they work, common types of Trojan malware, how Trojans are used, and how to protect yourself from Trojans. The report provides information on how Trojans can give attackers remote access and control over an infected computer without the user's knowledge to steal data or carry out other malicious activities. It describes some specific Trojans like backdoor and ransomware Trojans and explains how programs like Back Orifice work using a client-server model to control an infected machine remotely.
Information security
Information securityJAMEEL AHMED KHOSO The document discusses various types of digital threats, particularly focusing on worm viruses and trojans, detailing their mechanics, propagation methods, and potential damages they can cause to computer systems. It also outlines strategies for detecting infections and implementing access control security measures to mitigate these risks. The importance of preventive strategies, such as avoiding suspicious emails and regular software updates, is emphasized as key to maintaining cybersecurity.
The trojan horse virus
The trojan horse virusHTS Hosting The document discusses the Trojan horse virus, a type of malware that disguises itself as legitimate software to gain unauthorized access to users' systems. It outlines the various types of Trojans, their actions, characteristics, and the potential damage they can cause, such as stealing sensitive data and compromising network security. Emphasis is placed on the importance of cybersecurity measures to protect against such threats as internet usage increases.
Trojan backdoors
Trojan backdoorsseth edmond This document discusses Trojan horse programs and remote administration tools. It defines Trojan horses as programs that appear harmless but have malicious code. Trojan horses can give intruders access to computers by installing backdoors. Remote administration tools also allow unauthorized access and control of victim's computers. The document provides examples of common Trojan horses and remote access programs like Back Orifice and describes how to detect and remove such threats.
Security threats
Security threatsQamar Farooq Bots are malicious programs that infect computers without the owner's permission and join networks of infected machines called botnets. Botnets are then used by cybercriminals to carry out illegal activities like spamming, denial of service attacks, and identity theft. Criminals infect machines using techniques like exploiting vulnerabilities on websites or getting users to download Trojan horse programs disguised as other files. The bots communicate with command and control servers operated by the criminals to receive instructions. Activities facilitated by botnets include large-scale spamming, hosting phishing websites, and distributed denial of service attacks.
Trojan virus & backdoors
Trojan virus & backdoorsShrey Vyas This document discusses trojans and backdoors. It defines a trojan as a malicious program that misrepresents itself as useful to install itself on a victim's computer. Trojans are used for destructive purposes like crashing systems or stealing data, or for using the computer's resources. Examples of trojans provided include Netbus and Back Orifice. Backdoors are methods of bypassing authentication to gain unauthorized access. They work by installing hidden server software that listens for connections from client software controlled by attackers. Known backdoors discussed include Back Orifice and a possible NSA backdoor in a cryptographic standard.
Ethical hacking trojans, worms and spyware
Ethical hacking trojans, worms and spywaremissstevenson01 Trojans are malware that disguise themselves as legitimate programs to trick users into downloading and installing them. Once installed, they can allow hackers access and perform malicious activities like stealing data. Worms are standalone malware that spread automatically without needing user interaction. Ransomware encrypts users' files and demands payment for their return. Spyware secretly monitors users' online activities through keyloggers, hijacking webcams and microphones, and cracking passwords using dictionary attacks.
SECURITY THREATS AND SAFETY MEASURES
SECURITY THREATS AND SAFETY MEASURESShyam Kumar Singh This document discusses various types of cyber threats including viruses, worms, Trojan horses, spyware, malware, spam, and hackers/crackers. It defines each threat and provides examples. Viruses are programs that insert copies of themselves into other files or programs to spread. Worms replicate themselves across networks to spread. Trojan horses disguise themselves as useful programs but introduce viruses. Spyware monitors users' online activity without consent. Malware is any unwanted software intended to cause harm. Spam is unsolicited bulk email used for deception. Hackers and crackers aim to gain unauthorized access to systems for malicious purposes like theft. Antivirus tools can help protect against these cyber threats.
Ransomware hostage rescue manual
Ransomware hostage rescue manualRoel Palmaers The document is a ransomware hostage rescue manual that explains what ransomware is, how to identify if you're infected, and the steps to take if infected. It covers infection methods, response strategies, and preventive measures, emphasizing the importance of backups and security awareness. Additionally, it provides insights into Bitcoin and the use of the Tor network by hackers for anonymity.
attack vector in cyber security access to a computer
attack vector in cyber security access to a computerpremalathav6 An attack vector is a means through which attackers gain access to computers or networks to deliver malicious outcomes, exploiting vulnerabilities, including human errors. Common attack vectors include email phishing, malicious attachments, deception, hacking, counterfeit websites, worms, malicious macros, foistware, and viruses. Each method poses unique risks and typically requires user interaction or system vulnerabilities to be successful.
Computer virus
Computer virussajeena81 This document discusses computer viruses, malware, and types of malware such as viruses, worms, trojans, spyware, ransomware, and cryptojacking malware. It provides details on how viruses and malware spread and infect systems. It outlines common symptoms of a virus attack such as slowed system speed, pop-up windows, and potential device crashing. It also describes how to categorize malware based on how it spreads and what actions it performs after infecting a system. Specific types of trojans like backdoor, banker, and dropper trojans are outlined. Signs of a spyware infection and examples of historic malware like ILOVEYOU and Conficker are also mentioned.
Computer crimes
Computer crimesMuniba Bukhari This document discusses network and internet security and types of cyber crimes. It notes that while computers can be used for good or bad, some people use them to carry out illegal activities known as computer crimes. It then describes different types of perpetrators of cyber crimes like hackers, crackers, script kiddies, corporate spies, unethical employees, cyberextortionists, and cyberterrorists. The document also provides details on different types of computer viruses like worms, Trojan horses, macros, and boot sector viruses. It explains concepts like logic bombs, time bombs, data diddling, data stealing, and software piracy.
Dickmaster
DickmasterDickMaster1 This document defines and describes various types of malware including viruses, worms, Trojans, spyware, adware, backdoors, rootkits, and keyloggers. It provides examples of specific malware like the Melissa virus, Blaster worm, Magic Lantern keylogger software, and DarkComet remote administration tool. Malware is software designed to damage computers that can spread by inserting copies of itself into other programs and files.
It act seminar
It act seminarAkshay Sharma This document discusses Trojan horses, which are unauthorized programs that perform unwanted functions on a user's computer. It defines Trojans and explains how they work, providing examples of common Trojans like remote access Trojans and password stealing Trojans. The document also outlines how Trojans are transmitted and describes ways for users to obtain and install a Trojan on another person's computer without their consent.
Virus trojanworm
Virus trojanwormJenMorri A computer worm is a standalone malware program that replicates itself to spread to other computers, often using security failures to access targets without needing to attach to other programs like viruses. Worms usually harm networks through consuming bandwidth, and as incidents increase it is important to protect businesses with internet presences from the monetary losses caused, estimated at $1 billion per occurrence.
Type of Malware and its different analysis and its types !
Type of Malware and its different analysis and its types !Mohammed Jaseem Tp This document discusses different types of malware and methods for analyzing malware. It defines malware as malicious software designed to damage computers without consent. The document outlines 10 main types of malware: viruses, worms, Trojans, spyware, adware, ransomware, rootkits, keyloggers, botnets, and bugs. It also describes 3 methods of malware analysis: static analysis, which examines code without executing it; dynamic analysis, which observes behavior by running malware; and threat analysis, which identifies malware families and tracks criminal infrastructure over time.
4 threatsandvulnerabilities
4 threatsandvulnerabilitiesricharddxd The document defines threats, vulnerabilities, and various types of malware such as viruses, worms, and Trojans. It provides examples of how malware like the ILOVEYOU virus and Sasser worm spread and caused damage. The document also discusses how compromised computers can be used in botnets for spamming and denial of service attacks. It concludes with recommendations on security best practices like keeping systems updated, using antivirus software, and practicing cyber awareness.
Trojan Backdoors
Trojan BackdoorsJauwadSyed The document provides an in-depth overview of Trojan horse programs, explaining their function as deceptive software that grants unauthorized access to computer systems. It classifies Trojan payloads into seven types, detailing their potential harm and methods of infection. Additionally, it outlines preventive measures and removal strategies, emphasizing the distinction between viruses and Trojans, as well as the emerging threat of blended threats that combine various malicious attack methods.
Presentation Virus (salami attack and trojan horse)
Presentation Virus (salami attack and trojan horse)siti zulaikha Viruses are malicious computer programs that can spread from one computer to another by infecting files. They typically spread through removable media like floppy disks, downloading infected files from the internet or email attachments, or installing software that contains viruses. Common types of viruses include Trojan horses, which are programs that perform unauthorized actions without the user's knowledge or consent, and worms, which can spread automatically to other computers. Salami attacks involve small, unnoticeable changes like deducting small amounts of money from many accounts to carry out financial crimes without detection.
Ad
More from jyoti_lakhani (20)
CG02 Computer Graphic Systems.ppsx
CG02 Computer Graphic Systems.ppsxjyoti_lakhani The document discusses cathode ray tubes (CRTs) and how they work to display images on screens. It describes how CRTs use an electron gun to produce a scanning electron beam that hits a phosphorescent screen, causing spots of light. Different phosphors allow for different colors. The beam is focused and deflected electromagnetically to refresh the screen rapidly and create a full image. Resolution depends on factors like phosphor type and beam intensity. Color images are represented using RGB color models that mix red, green, and blue intensities.
Projections.pptx
Projections.pptxjyoti_lakhani Projection is a technique to transform a 3D object into a 2D plane. There are two main types of projection: parallel projection and perspective projection. Parallel projection involves projecting lines parallel to the view plane, maintaining accurate measurements but less realistic appearance. Perspective projection accounts for the finite distance to the view plane, making images more realistic but challenging to implement due to vanishing points. Common parallel projections include orthographic and oblique, while common perspective projections include one point, two point, and three point perspectives.
CG04 Color Models.ppsx
CG04 Color Models.ppsxjyoti_lakhani The document discusses three color models:
1) RGB color model represents colors as combinations of red, green, and blue primary colors. It can be represented as a color cube with these primary colors at the vertices.
2) CMY color model uses cyan, magenta, and yellow primaries and subtracts from white to produce colors.
3) HSV color model describes colors in terms of hue, saturation, and value. Hue is represented as an angle around a hexagonal boundary in a three-dimensional hexcone shape. Saturation corresponds to purity and value corresponds to intensity.
CG03 Random Raster Scan displays and Color CRTs.ppsx
CG03 Random Raster Scan displays and Color CRTs.ppsxjyoti_lakhani The document discusses different types of graphics displays. It describes raster-scan displays, which use an electron beam that sweeps across the screen from top to bottom to display an image. Picture definition is stored in a frame buffer. It also describes random-scan displays, which direct the electron beam only where lines need to be drawn. Color CRT monitors use phosphors and a shadow mask to display color. Flat panel displays like plasma panels, thin-film electroluminescent displays, and liquid crystal displays provide thinner alternatives to CRTs.
CG02 Computer Graphic Systems.pptx
CG02 Computer Graphic Systems.pptxjyoti_lakhani The document discusses cathode ray tubes (CRTs) and how they work to display images on monitors. It describes how CRTs use an electron gun to produce a scanning electron beam that hits a phosphorescent screen, causing spots of light. Different phosphors allow for different colors. The beam is swept across the screen in a raster pattern through deflection coils. Factors like resolution, aspect ratio, and refresh rate affect image quality. Color images are represented using the RGB color model with red, green, and blue intensity values.
CG01 introduction.ppsx
CG01 introduction.ppsxjyoti_lakhani The document discusses computer graphics and the process of generating images through different stages: object space defines the envisioned drawing, image space is the continuous space containing the drawn object, and scan conversion converts it to discrete pixels on a screen causing aliasing. It also describes computer graphics tools including hardware like monitors and software like graphics routines and standards used to produce pictures. Finally, it outlines applications of computer graphics in engineering, medical visualization, animation, and more.
Doubly linked list
Doubly linked listjyoti_lakhani A doubly linked list is a type of linked list that allows navigation in both directions via previous and next pointers. It supports insertion and deletion at both the front and rear of the list. The document outlines the process for inserting and deleting nodes from a doubly linked list, including handling empty and non-empty list cases.
Double ended queue
Double ended queuejyoti_lakhani A double-ended queue (DEQueue) allows nodes to be added and removed from both the front and rear ends. It supports four basic operations - insertion and deletion from the front and rear. The document describes the DEQueue data structure and provides pseudocode for handling cases when inserting or deleting from an empty versus non-empty queue.
Tree terminology and introduction to binary tree
Tree terminology and introduction to binary treejyoti_lakhani Trees are hierarchical data structures where data items have a parent-child relationship. There are several ways to represent trees in memory, including array and linked list representations. Array representation stores tree nodes sequentially in an array, where the index of each node can be used to determine its parent, left child, right child, and siblings according to specific formulas. For example, the parent of node at index n is located at (n-1)/2, the left child is at 2n+1, and the right child is at 2n+2. Array representation allows trees to be traversed and manipulated efficiently.
Priority queue
Priority queuejyoti_lakhani A priority queue is a queue that allows nodes to be added and deleted based on priority or preference. Nodes with higher priority are inserted at the front of the queue and lower priority nodes are added to the back. When deleting from the queue, the highest priority or first node is always removed first.
Ds006 linked list- delete from front
Ds006 linked list- delete from frontjyoti_lakhani This C++ program implements functions to perform operations on a singly linked list:
1. A create_node function allocates and returns a new node with the given value.
2. An insert_begin function inserts a new node at the beginning of the list, updating the start pointer.
3. A delete_begin function deletes the node at the beginning of the list, updating the start pointer and deallocating the node.
4. A display function traverses the list and prints out the values of each node.
Ds06 linked list- insert a node after a given node
Ds06 linked list- insert a node after a given nodejyoti_lakhani The document discusses inserting a node into a linked list after a given node. It describes linked lists as a linear data structure that stores multiple values in nodes connected by pointers. The algorithm for inserting a node after a given node is presented:
1. Find the node before the given node by traversing the list and comparing node values
2. Set the next pointer of the new node to the node after the given node
3. Set the next pointer of the node before the given node to the new node
This inserts the new node between the node before and after the given node in the linked list.
Ds06 linked list- insert a node at end
Ds06 linked list- insert a node at endjyoti_lakhani This document discusses inserting a node into a linked list at the end. It explains that to insert a node at the end, you first check if the list is empty and if so make the new node the start. If the list is not empty, you iterate through the list with a pointer ptr until ptr->next is NULL, at which point you set ptr->next to the new node and new_node->next to NULL. Diagrams are included to visualize the process. The algorithm runs in O(n) time where n is the number of nodes in the list.
Ds06 linked list- insert a node at beginning
Ds06 linked list- insert a node at beginningjyoti_lakhani The document discusses linked lists and operations on linked lists such as insertion and deletion of nodes. It specifically describes an algorithm to insert a node at the beginning of a linked list. The algorithm first checks if the list is empty, and if so makes the new node the start. If the list is not empty, it sets the next pointer of the new node to the current start node, and then makes the new node the new start.
Ds06 linked list- intro and create a node
Ds06 linked list- intro and create a nodejyoti_lakhani A linked list is a linear data structure that stores multiple values in nodes that are connected by pointers. Each node contains a data field for its value and a pointer field linking to the next node. This allows flexible and efficient insertion and removal of nodes anywhere in the list. The document outlines the basic structure of a linked list and node, and provides pseudocode for creating a new node by allocating memory, inserting the data value, and initializing the next pointer to NULL.
Ds04 abstract data types (adt) jyoti lakhani
Ds04 abstract data types (adt) jyoti lakhanijyoti_lakhani An abstract data type (ADT) defines a pen as a collection of related data items including type, brand, color, and price along with operations such as write. An ADT describes what data and operations are involved without specifying how they are implemented, focusing on the essential properties and behaviors. A data structure then provides the physical implementation of an ADT, realizing how the data and operations are structured and processed.
Ds03 part i algorithms by jyoti lakhani
Ds03 part i algorithms by jyoti lakhanijyoti_lakhani The document defines an algorithm as a finite sequence of unambiguous instructions to solve a problem and produce an output from given inputs. It notes that algorithms have advantages like being easy to plan, implement, understand and debug. The key aspects of algorithms discussed are that they must be step-by-step, unambiguous and able to solve problems in a finite amount of time. The document also discusses analyzing and choosing between algorithms, as well as designing, proving, coding and analyzing algorithms.
Ds03 algorithms jyoti lakhani
Ds03 algorithms jyoti lakhanijyoti_lakhani The document discusses algorithms, defining them as unambiguous step-by-step instructions to solve a problem within a finite time. It notes that algorithms can be represented in various ways like pseudo-code or flowcharts. The key aspects of algorithms covered include analyzing their time and space complexity, choosing appropriate data structures, proving their correctness, and coding them efficiently. The document emphasizes understanding the problem fully before designing an algorithm and choosing techniques like greedy or divide-and-conquer approaches.
Ds02 flow chart and pseudo code
Ds02 flow chart and pseudo codejyoti_lakhani The document discusses flow charts and pseudo code. It provides an overview of flow chart symbols and conventions, examples of algorithms expressed as both a flow chart and pseudo code, guidelines for writing pseudo code, and conventions commonly used in pseudo code.
Ds01 data structure introduction - by jyoti lakhani
Ds01 data structure introduction - by jyoti lakhanijyoti_lakhani The document discusses data structures and algorithms. It explains that data structures organize data in a way that makes it easy to access, manipulate, and update. Using the correct data structure for a problem makes the problem more manageable and finding a solution easier. Algorithms provide step-by-step instructions to solve problems and are implemented using data structures. They allow complex problems to be broken down into smaller, modular problems.
Ad
Recently uploaded (20)
FIDO Seminar: Perspectives on Passkeys & Consumer Adoption.pptx
FIDO Seminar: Perspectives on Passkeys & Consumer Adoption.pptxFIDO Alliance FIDO Seminar: Perspectives on Passkeys & Consumer Adoption
Providing an OGC API Processes REST Interface for FME Flow
Providing an OGC API Processes REST Interface for FME FlowSafe Software This presentation will showcase an adapter for FME Flow that provides REST endpoints for FME Workspaces following the OGC API Processes specification. The implementation delivers robust, user-friendly API endpoints, including standardized methods for parameter provision. Additionally, it enhances security and user management by supporting OAuth2 authentication. Join us to discover how these advancements can elevate your enterprise integration workflows and ensure seamless, secure interactions with FME Flow.
AudGram Review: Build Visually Appealing, AI-Enhanced Audiograms to Engage Yo...
AudGram Review: Build Visually Appealing, AI-Enhanced Audiograms to Engage Yo...SOFTTECHHUB AudGram changes everything by bridging the gap between your audio content and the visual engagement your audience craves. This cloud-based platform transforms your existing audio into scroll-stopping visual content that performs across all social media platforms.
Crypto Super 500 - 14th Report - June2025.pdf
Crypto Super 500 - 14th Report - June2025.pdfStephen Perrenod This OrionX's 14th semi-annual report on the state of the cryptocurrency mining market. The report focuses on Proof-of-Work cryptocurrencies since those use substantial supercomputer power to mint new coins and encode transactions on their blockchains. Only two make the cut this time, Bitcoin with $18 billion of annual economic value produced and Dogecoin with $1 billion. Bitcoin has now reached the Zettascale with typical hash rates of 0.9 Zettahashes per second. Bitcoin is powered by the world's largest decentralized supercomputer in a continuous winner take all lottery incentive network.
“Addressing Evolving AI Model Challenges Through Memory and Storage,” a Prese...
“Addressing Evolving AI Model Challenges Through Memory and Storage,” a Prese...Edge AI and Vision Alliance For the full video of this presentation, please visit: https://www.edge-ai-vision.com/2025/06/addressing-evolving-ai-model-challenges-through-memory-and-storage-a-presentation-from-micron/
Wil Florentino, Senior Segment Marketing Manager at Micron, presents the “Addressing Evolving AI Model Challenges Through Memory and Storage” tutorial at the May 2025 Embedded Vision Summit.
In the fast-changing world of artificial intelligence, the industry is deploying more AI compute at the edge. But the growing diversity and data footprint of transformers and models such as large language models and large multimodal models puts a spotlight on memory performance and data storage capacity as key bottlenecks. Enabling the full potential of AI in industries such as manufacturing, automotive, robotics and transportation will require us to find efficient ways to deploy this new generation of complex models.
In this presentation, Florentino explores how memory and storage are responding to this need and solving complex issues in the AI market. He examines the storage capacity and memory bandwidth requirements of edge AI use cases ranging from tiny devices with severe cost and power constraints to edge servers, and he explains how new memory technologies such as LPDDR5, LPCAMM2 and multi-port SSDs are helping system developers to meet these challenges.
Security Tips for Enterprise Azure Solutions
Security Tips for Enterprise Azure SolutionsMichele Leroux Bustamante Delivering solutions to Azure may involve a variety of architecture patterns involving your applications, APIs data and associated Azure resources that comprise the solution. This session will use reference architectures to illustrate the security considerations to protect your Azure resources and data, how to achieve Zero Trust, and why it matters. Topics covered will include specific security recommendations for types Azure resources and related network security practices. The goal is to give you a breadth of understanding as to typical security requirements to meet compliance and security controls in an enterprise solution.
FME for Good: Integrating Multiple Data Sources with APIs to Support Local Ch...
FME for Good: Integrating Multiple Data Sources with APIs to Support Local Ch...Safe Software Have-a-skate-with-Bob (HASB-KC) is a local charity that holds two Hockey Tournaments every year to raise money in the fight against Pancreatic Cancer. The FME Form software is used to integrate and exchange data via API, between Google Forms, Google Sheets, Stripe payments, SmartWaiver, and the GoDaddy email marketing tools to build a grass-roots Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system for the charity. The CRM is used to communicate effectively and readily with the participants of the hockey events and most importantly the local area sponsors of the event. Communication consists of a BLOG used to inform participants of event details including, the ever-important team rosters. Funds raised by these events are used to support families in the local area to fight cancer and support PanCan research efforts to find a cure against this insidious disease. FME Form removes the tedium and error-prone manual ETL processes against these systems into 1 or 2 workbenches that put the data needed at the fingertips of the event organizers daily freeing them to work on outreach and marketing of the events in the community.
War_And_Cyber_3_Years_Of_Struggle_And_Lessons_For_Global_Security.pdf
War_And_Cyber_3_Years_Of_Struggle_And_Lessons_For_Global_Security.pdfbiswajitbanerjee38 Russia is one of the most aggressive nations when it comes to state coordinated cyberattacks — and Ukraine has been at the center of their crosshairs for 3 years. This report, provided the State Service of Special Communications and Information Protection of Ukraine contains an incredible amount of cybersecurity insights, showcasing the coordinated aggressive cyberwarfare campaigns of Russia against Ukraine.
It brings to the forefront that understanding your adversary, especially an aggressive nation state, is important for cyber defense. Knowing their motivations, capabilities, and tactics becomes an advantage when allocating resources for maximum impact.
Intelligence shows Russia is on a cyber rampage, leveraging FSB, SVR, and GRU resources to professionally target Ukraine’s critical infrastructures, military, and international diplomacy support efforts.
The number of total incidents against Ukraine, originating from Russia, has steadily increased from 1350 in 2021 to 4315 in 2024, but the number of actual critical incidents has been managed down from a high of 1048 in 2022 to a mere 59 in 2024 — showcasing how the rapid detection and response to cyberattacks has been impacted by Ukraine’s improved cyber resilience.
Even against a much larger adversary, Ukraine is showcasing outstanding cybersecurity, enabled by strong strategies and sound tactics. There are lessons to learn for any enterprise that could potentially be targeted by aggressive nation states.
Definitely worth the read!
June Patch Tuesday
June Patch TuesdayIvanti Ivanti’s Patch Tuesday breakdown goes beyond patching your applications and brings you the intelligence and guidance needed to prioritize where to focus your attention first. Catch early analysis on our Ivanti blog, then join industry expert Chris Goettl for the Patch Tuesday Webinar Event. There we’ll do a deep dive into each of the bulletins and give guidance on the risks associated with the newly-identified vulnerabilities.
vertical-cnc-processing-centers-drillteq-v-200-en.pdf
vertical-cnc-processing-centers-drillteq-v-200-en.pdfAmirStern2 מכונות CNC קידוח אנכיות הן הבחירה הנכונה והטובה ביותר לקידוח ארונות וארגזים לייצור רהיטים. החלק נוסע לאורך ציר ה-x באמצעות ציר דיגיטלי מדויק, ותפוס ע"י צבת מכנית, כך שאין צורך לבצע setup (התאמות) לגדלים שונים של חלקים.
“Why It’s Critical to Have an Integrated Development Methodology for Edge AI,...
“Why It’s Critical to Have an Integrated Development Methodology for Edge AI,...Edge AI and Vision Alliance For the full video of this presentation, please visit: https://www.edge-ai-vision.com/2025/06/why-its-critical-to-have-an-integrated-development-methodology-for-edge-ai-a-presentation-from-lattice-semiconductor/
Sreepada Hegade, Director of ML Systems and Software at Lattice Semiconductor, presents the “Why It’s Critical to Have an Integrated Development Methodology for Edge AI” tutorial at the May 2025 Embedded Vision Summit.
The deployment of neural networks near sensors brings well-known advantages such as lower latency, privacy and reduced overall system cost—but also brings significant challenges that complicate development. These challenges can be addressed effectively by choosing the right solution and design methodology. The low-power FPGAs from Lattice are well poised to enable efficient edge implementation of models, while Lattice’s proven development methodology helps to mitigate the challenges and risks associated with edge model deployment.
In this presentation, Hegade explains the importance of an integrated framework that tightly consolidates different aspects of edge AI development, including training, quantization of networks for edge deployment, integration with sensors and inferencing. He also illustrates how Lattice’s simplified tool flow helps to achieve the best trade-off between power, performance and efficiency using low-power FPGAs for edge deployment of various AI workloads.
FIDO Seminar: Authentication for a Billion Consumers - Amazon.pptx
FIDO Seminar: Authentication for a Billion Consumers - Amazon.pptxFIDO Alliance FIDO Seminar: Authentication for a Billion Consumers - Amazon
Bridging the divide: A conversation on tariffs today in the book industry - T...
Bridging the divide: A conversation on tariffs today in the book industry - T...BookNet Canada A collaboration-focused conversation on the recently imposed US and Canadian tariffs where speakers shared insights into the current legislative landscape, ongoing advocacy efforts, and recommended next steps. This event was presented in partnership with the Book Industry Study Group.
Link to accompanying resource: https://bnctechforum.ca/sessions/bridging-the-divide-a-conversation-on-tariffs-today-in-the-book-industry/
Presented by BookNet Canada and the Book Industry Study Group on May 29, 2025 with support from the Department of Canadian Heritage.
Viral>Wondershare Filmora 14.5.18.12900 Crack Free Download
Viral>Wondershare Filmora 14.5.18.12900 Crack Free DownloadPuppy jhon ➡ 🌍📱👉COPY & PASTE LINK👉👉👉 ➤ ➤➤ https://drfiles.net/
Wondershare Filmora Crack is a user-friendly video editing software designed for both beginners and experienced users.
Artificial Intelligence in the Nonprofit Boardroom.pdf
Artificial Intelligence in the Nonprofit Boardroom.pdfOnBoard OnBoard recently partnered with Microsoft Tech for Social Impact on the AI in the Nonprofit Boardroom Survey, an initiative designed to uncover the current and future role of artificial intelligence in nonprofit governance.
Tech-ASan: Two-stage check for Address Sanitizer - Yixuan Cao.pdf
Tech-ASan: Two-stage check for Address Sanitizer - Yixuan Cao.pdfcaoyixuan2019 A presentation at Internetware 2025.
Can We Use Rust to Develop Extensions for PostgreSQL? (POSETTE: An Event for ...
Can We Use Rust to Develop Extensions for PostgreSQL? (POSETTE: An Event for ...NTT DATA Technology & Innovation Can We Use Rust to Develop Extensions for PostgreSQL?
(POSETTE: An Event for Postgres 2025)
June 11, 2025
Shinya Kato
NTT DATA Japan Corporation
FIDO Seminar: New Data: Passkey Adoption in the Workforce.pptx
FIDO Seminar: New Data: Passkey Adoption in the Workforce.pptxFIDO Alliance FIDO Seminar: New Data: Passkey Adoption in the Workforce
“Addressing Evolving AI Model Challenges Through Memory and Storage,” a Prese...
“Addressing Evolving AI Model Challenges Through Memory and Storage,” a Prese...Edge AI and Vision Alliance
“Why It’s Critical to Have an Integrated Development Methodology for Edge AI,...
“Why It’s Critical to Have an Integrated Development Methodology for Edge AI,...Edge AI and Vision Alliance
Can We Use Rust to Develop Extensions for PostgreSQL? (POSETTE: An Event for ...
Can We Use Rust to Develop Extensions for PostgreSQL? (POSETTE: An Event for ...NTT DATA Technology & Innovation
Ids 007 trojan horse
- 1. Trojan
- 2. A malware which misleads users of its true intent. The term is derived from the Ancient Greek story of Trojan Horse that led to the fall of the city of Troy Trojans are generally spread by – - a user is duped into executing an email attachment disguised to appear not suspicious, (e.g., a routine form to be filled in) - by clicking on some fake advertisement Their payload act as a backdoor, contacting a controller which can then have unauthorized access to the affected computer. Trojan
- 3. Unlike computer viruses and worms, trojans generally do not attempt to inject themselves into other files Trojan viruses, in this way, may require interaction with a malicious controller (not necessarily distributing the trojan) to fulfill their purpose. It is possible for those involved with trojans to scan computers on a network to locate any with a trojan installed, which the hacker can then control, creating a so called botnet. A botnet is a number of Internet-connected devices, each of which is running one or more bots. Botnets can be used to perform Distributed Denial-of- Service (DDoS) attacks, steal data, send spam, and allow the attacker to access the device and its connection. The owner can control the botnet using command and control (C&C) software Trojans may allow an attacker to access users' personal information such as banking information, passwords, or personal identity. It can also delete a user's files or infect other devices connected to the network. Ransomware attacks are often carried out using a trojan.
- 4. Some trojans take advantage of a security flaw in older versions of Internet Explorer and Google Chrome to use the host computer as an anonymizer proxy to effectively hide Internet usage, enabling the controller to use the Internet for illegal purposes while all potentially incriminating evidence indicates the infected computer or its IP address. An anonymizer proxy is a tool that attempts to make activity on the Internet untraceable. It is a proxy server computer that acts as an intermediary and privacy shield between a client computer and the rest of the Internet. It accesses the Internet on the user's behalf, protecting personal information of the user by hiding the client computer's identifying information
- 5. According to a survey conducted by BitDefender from January to June 2009, "trojan-type malware is on the rise, accounting for 83% of the global malware detected in the world." Trojans have a relationship with worms, as they spread with the help given by worms and travel across the internet with them. The host's computer may or may not show the internet history of the sites viewed using the computer as a proxy. The first generation of anonymizer trojan horses tended to leave their tracks in the page view histories of the host computer. Later generations of the trojan tend to "cover" their tracks more efficiently.
- 6. Examples of Trojan Horse Virus Infection Trojan Infection Exploit Backdoor Rootkit Trojan Banker Trojan DDoS Trojan Downloa der Trojan Dropper
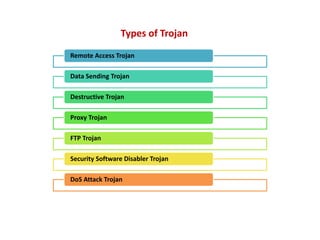
- 7. Remote Access Trojan Data Sending Trojan Destructive Trojan Proxy Trojan FTP Trojan Security Software Disabler Trojan DoS Attack Trojan Types of Trojan
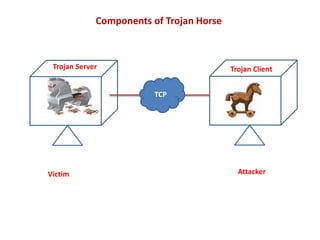
- 8. Victim Attacker TCP Trojan Server Trojan Client Components of Trojan Horse
- 9. Zeus Zeus is a Trojan horse made to infect Windows computers so that it will perform various criminal tasks. The most common of these tasks are usually man-in-the-browser keylogging and form grabbing. The majority of computers were infected either through drive-by downloads or phishing scams. First identified in 2009, it managed to compromise thousands of FTP accounts and computers from large multinational corporations and banks such as Amazon, Oracle, Bank of America, Cisco, etc. Controllers of the Zeus botnet used it to steal the login credentials of social network, email and banking accounts.
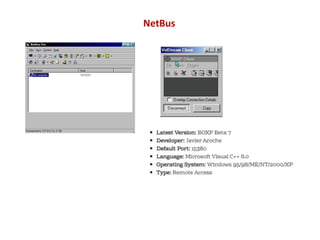
- 10. NetBus
- 11. Back Orifice XP
- 12. Sub Seven (Sub7)
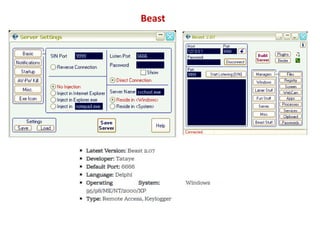
- 13. Beast
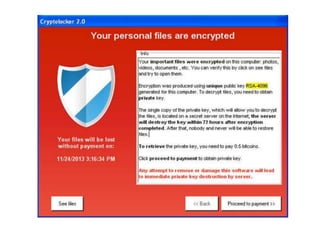
- 14. CryptoLocker CryptoLocker is a form of Trojan horse ransomware targeted at computers running Windows. It uses several methods to spread itself, such as email, and once a computer is infected, it will proceed to encrypt certain files on the hard drive and any mounted storage connected to it with RSA public key cryptography. While it is easy enough to remove the malware from the computer, the files will still remain encrypted. The only way to unlock the files is to pay a ransom by a deadline. If the deadline is not met, the ransom will increase significantly or the decryption keys deleted. The ransom usually amount to $400 in prepaid cash or bitcoin.
- 16. Flashback • One of the few Mac malware • It showed that Macs are not immune. • The Trojan was first discovered in 2011 by antivirus company Intego as a fake Flash install. • In its newer incarnation, a user simply needs to have Java enabled. It propagates itself by using compromised websites containing JavaScript code that will download the payload. Once installed, the Mac becomes part of a botnet of other infected Macs.