What is-twamp
8 likes19,348 views
The presentation explains about TWAMP and its effective standard-based method for monitoring performance in IP networks.
1 of 11
Downloaded 376 times






Ad
Recommended
Introduction to 5G NR



Introduction to 5G NRAbhijeet Kumar This document provides an introduction to 5G technology, including:
- 5G aims to meet growing connectivity needs and fulfill diverse use cases such as drones, augmented reality, and the Internet of Things.
- 5G standards are being developed by 3GPP and ITU, with 3GPP specifying the radio technology beyond LTE known as New Radio (NR).
- 5G requirements defined by 3GPP include high peak data rates, low latency, high reliability, large connection densities, and support for high mobility.
5gc call flow



5gc call flowKoorosh Hoveyda The document describes the 5G registration process between a UE and AMF. It involves the following key steps:
1. The UE sends a registration request to the AMF via the (R)AN.
2. The AMF authenticates the UE and retrieves subscription data. If a new AMF is selected, it retrieves the UE context from the old AMF.
3. If registration is successful, the AMF sends a registration accept message to the UE to complete the process. It also notifies other network functions like SMFs and PCF.
5g introduction_NR



5g introduction_NRNitin George Thomas The document provides an introduction to 5G architecture and use cases. It discusses how 5G aims to support services with diverse requirements through enhanced mobile broadband, massive machine type communication, and ultra-reliable low latency communication. 5G will have several deployment scenarios including non-standalone using LTE infrastructure initially, and standalone 5G networks. The core network is expected to see the most radical innovation since 2G, moving to a cloud-native architecture with network slicing, separation of control and user plane, and network functions that can be deployed flexibly. The smart grid is presented as a challenging use case that may benefit from 5G capabilities such as low latency and connectivity of millions of devices.
5 g core overview



5 g core overviewHemraj Kumar The document provides an overview of 3GPP 5G Core network architecture. Some key points:
- It defines a service-based architecture with network functions that expose capabilities via REST APIs.
- Control and user plane functions are separated for independent scalability. Functions are also modularized to enable network slicing.
- The 5G core network supports features like edge computing, network slicing, mobility management, and session management.
- It evolves from previous generations with a cloud-native design, virtualization, and exposure of capabilities via APIs.
5G Basic Call Flows.pdf



5G Basic Call Flows.pdfIbrahimSayed61 The document describes the 5G registration process between a UE and an AMF. It involves the following key steps:
1. The UE sends a registration request to the AMF via the (R)AN.
2. The AMF authenticates the UE and retrieves subscription data. If a new AMF is selected, it retrieves the UE context from the old AMF.
3. If registration is successful, the AMF sends a registration accept message to the UE to complete the process. It also notifies other network functions like SMFs and PCF.
5 g core network and the cloud - A standards perspective



5 g core network and the cloud - A standards perspectiveSridhar Bhaskaran A presentation on the 5G Core Network Architecture (based on 3GPP Release 15) and architectural enablers for cloud deployments
Lte irat-troubleshooting-guide



Lte irat-troubleshooting-guideDenmark Wilson This document provides a troubleshooting guide for LTE inter-radio access technology (IRAT) handovers. It describes why IRAT is needed as voice revenues remain important while data revenues grow. It also outlines the applications of IRAT, delivery policies for idle mode, connected mode, and voice services. Signaling procedures for IRAT handovers including reselection, redirection, and PS handover are defined. Key performance indicators for IRAT including control plane delays and user plane interruption times are also defined to help diagnose IRAT issues.
5G Standards: 3GPP Release 15, 16, and beyond



5G Standards: 3GPP Release 15, 16, and beyond3G4G Presented by Sasha Sirotkin, Vice Chairman of 3GPP RAN3 at Wireless Russia, May 2019
*** Shared with Permission ***
Volte troubleshooting



Volte troubleshootingJamil Awan The document discusses VoLTE optimization services including RAN and EPC analysis using various tools. It details accomplishments like optimizing sites for carriers and analyzing problems like VoLTE drop issues. The key services described are VoLTE parameter audits, drive log analysis, UETR analysis, and end-to-end VoLTE call tracing. Case studies provided examine issues like QCI profile not defined, RRC drops without VoLTE drops, and improvements gained from features like ICIC and parameter changes.
LTE Interference troubleshooting guide



LTE Interference troubleshooting guideKlajdi Husi The document discusses fault analysis and troubleshooting of LTE antenna and feeder systems. It describes techniques like RSSI analysis, frequency scanning, interference detection tests, and DTP testing to identify issues like passive intermodulation (PIM) and determine if the fault is in the antenna tower or below. Parameters for simulated load testing and online interference monitoring are also outlined.
UMTS/LTE/EPC Call Flows for CSFB



UMTS/LTE/EPC Call Flows for CSFBJustin MA (馬嘉昌) It is a handbook of UMTS/LTE/EPC CSFB call flows.
This document is originally edited by Justin MA and it is free to share to everyone who are interested.
All reference/resource are from internet. If there is any copy-right issue, please kindly inform Justin by majachang@gmail.com.
Thanks for your reading!
LTE Call Processing and Handover



LTE Call Processing and HandoverSitha Sok •CPS (Call Processing Software): LTE Control & Bearer Protocol processing
•OAM (Operation and Maintenance): eNB Operation and Maintenance
•MW (Middleware): IPC and Redundancy function
•IPRS (IP Routing Software): Routing protocol operation
•NP SW (Network Processor Software): Packet forwarding function
•OS (Operating System): Embedded Linux
•DD (Device Driver): initializing and setting the devices
5G_NR_Overview_Architecture_and_Operating_Modes



5G_NR_Overview_Architecture_and_Operating_ModesAalekh Jain 5G/NR wireless communication technology overview, architecture and its operating modes SA and NSA. Also an introduction to VoNR and other services overview of 5G network.
The key technologies of 5G namely MIMO and Network slicing are also explained.
5g architecture, Industrial Training



5g architecture, Industrial TrainingSumanPramanik7 The document discusses the evolution of network architectures from 2G to 5G. It describes the key network elements and interfaces in 2G, 3G, 4G and 5G networks. The 5G network architecture uses both a reference point architecture for the user plane and a service-based architecture for the control plane. The main network functions in the 5G control plane are the AMF, SMF, UDM, AUSF, NSSF, NEF, NRF and UDR. The UPF is the main network element in the user plane.
LTE and EPC Specifications



LTE and EPC Specificationsaliirfan04 This document outlines the 3GPP specifications process for developing new mobile network systems and features. It follows a three stage process:
Stage 1 defines service requirements. Stage 2 defines the network architecture, elements, and high-level flows. Stage 3 defines protocols, state machines, and messages.
This process was applied to developing LTE, where Stage 1 documents defined requirements like throughput rates and latency. Stage 2 documents described the overall LTE system architecture. Numerous Stage 3 specifications then defined the protocols that enable LTE.
Advanced: 5G Service Based Architecture (SBA)



Advanced: 5G Service Based Architecture (SBA)3G4G A quick look at 5G System architecture in Reference point representation and in Service Based representation and also look at the different Network Functions (NFs) within the 5G System.
Ericsson RBS 6000



Ericsson RBS 6000ibrahimnabil17 The document summarizes the Ericsson RBS6000 series of radio base stations, which were popular in the last decade. It describes the modular design using different units like Digital Units and Radio Units to support configurations. It provides examples of configurations including racks and shelves. It also describes the evolution of the GSM modules from early DUG10/RUG designs to later DUG20/RUS designs with baseband processing. UMTS and LTE modules are also introduced. Combined GSM/UMTS/LTE configurations using modules like DUS31/41 are highlighted. Finally it discusses opportunities for Osmocom software to support these radios by adding E1/TDM user plane support.
Lte basic parameters



Lte basic parametersLinh Phạm LTE uses various frequency bands and duplexing techniques to provide high-speed data and peak download speeds of up to 300 Mbps. It supports mobility of up to 350 km/h and uses advanced technologies like OFDM, SC-FDMA, MIMO and turbo coding to achieve low latency and high bandwidth. LTE specifications define channel bandwidths of 1.4, 3, 5, 10, 15 and 20 MHz with modulation schemes of QPSK, 16QAM and 64QAM.
Lte signaling



Lte signalingMansour Naslcheraghi The document provides an overview of cellular communications signaling for LTE, LTE-A, and 4G technologies. It describes the LTE architecture including functions of the evolved node B, mobility management entity, serving gateway, home subscriber server, and PDN gateway. It also provides details on the LTE physical layer including OFDMA modulation, reference signal measurements for handover, and an example handover procedure using the X2 interface. In conclusion, it discusses key criteria for designing handovers and aspects for further research.
LTE: X2 interface



LTE: X2 interfaceSchwannden Kuo The document discusses the X2 interface and X2 handover procedure in LTE networks. The X2 interface connects two neighboring eNodeBs and establishes an X2 connection through the X2 setup procedure. The X2 handover procedure allows handing over a UE's connection from a source eNodeB to a target eNodeB, involving preparation where the target allocates resources and the UE connects to it, and execution including a path switch to route data to the target eNodeB. Key information like UE context and bearers is exchanged between eNodeBs through the X2 interface to enable smooth handover.
Radio Measurements in LTE



Radio Measurements in LTESofian . The document discusses various LTE measurement parameters and procedures including:
1. The eNB reports a list of detected PRACH preambles and measures timing advance, average RSSI, average SINR, UL CSI, and transport BLER for RRM purposes.
2. UE measurements include CQI, RSRP, and RSRQ while eNB measurements include timing advance, RSSI, SINR, UL CSI, detected preambles, and transport BLER. Inter-RAT measurements are also discussed.
3. Examples of RSRP, RSRQ, and timing advance procedures are provided along with CQI measurement details. PLMN selection, cell selection,
Tti bundling in fdd and tdd



Tti bundling in fdd and tddLaxman Mewari TTI bundling is a technique used in LTE to improve uplink coverage for voice calls by transmitting the same transport block containing voice data over multiple consecutive subframes without waiting for HARQ feedback. This provides a coding gain of up to 4dB compared to single subframe transmission, allowing power-limited UEs at the cell edge to be received with sufficient quality. TTI bundling can be implemented in both FDD and TDD LTE networks but with some differences due to limitations on consecutive uplink subframes in TDD configurations. It provides lower latency voice transmission compared to alternatives like RLC segmentation while reducing overhead.
LTE optimization



LTE optimizationجامعة تعز كلية الهندسة وتقنية المعلومات Taiz University Engineering This document describes the design of an LTE network optimization project by a group of students from Taiz University. It includes an introduction to LTE, the network planning process, and LTE system architecture. The network planning section discusses coverage planning including link budget calculations and propagation models, as well as capacity planning considering factors like interference levels and supported modulation schemes. The document also provides an overview of LTE system architecture components including the user equipment, E-UTRAN, EPC, and functions of each. It concludes with a section on LTE radio frequency optimization methods.
Lte default and dedicated bearer / VoLTE



Lte default and dedicated bearer / VoLTEmanish_sapra LTE uses EPS bearers to carry user data traffic. There are two types of EPS bearers - default bearers and dedicated bearers. Default bearers are created for each PDN connection and provide basic "best effort" internet access. Dedicated bearers provide additional tunnels for specific traffic like VoLTE and can have guaranteed bitrates. Dedicated bearers are linked to a default bearer and inherit properties like the PDN address from the default bearer. GTP is the protocol used to encapsulate and carry bearer traffic through the LTE core network.
How to dimension user traffic in LTE



How to dimension user traffic in LTEAlthaf Hussain The document discusses how to characterize and dimension user traffic in 4G networks. It describes how to define data traffic in terms of data speed and data tonnage. Data speed is the rate at which data is transferred, while data tonnage refers to the total amount of data exchanged. The document provides examples of data speed metrics used in 3GPP standards and outlines factors to consider when calculating expected data usage per subscriber based on typical mobile application usage patterns and available data plans. Dimensioning user traffic accurately is important for designing 4G networks to meet capacity demands.
Anr feature in lte



Anr feature in lteLokendra Rathore The document discusses Ericsson's Automatic Neighbor Relation (ANR) feature. It explains that ANR improves network performance and reduces maintenance by automatically detecting, adding, and setting up neighbor relations between cells. This allows seamless handovers and prevents dropped calls when sites go down. The document outlines how ANR works for intra-frequency, inter-frequency, and inter-RAT neighbor detection in LTE, UTRAN, and GERAN networks. It also describes ANR parameters, functions, and the affected network features.
LTE KPI



LTE KPISitha Sok 1) The document describes key performance indicators (KPIs) for measuring the performance of an LTE radio network. It defines KPIs related to accessibility, retainability, mobility, and latency.
2) Accessibility KPIs measure aspects like call setup success rate, RRC setup success rate, and E-RAB setup success rate. Mobility KPIs evaluate handover success rates within LTE and between LTE and other technologies.
3) Retainability KPIs track metrics such as call drop rate and call setup completion rate. The document also provides details on how to calculate each KPI and which counters are needed to measure the underlying events.
5G NR: Key features and enhancements



5G NR: Key features and enhancements3G4G An overview of 5G NR key technical features and enhancements for massive MIMO, mmWave, etc.
Presented by Yinan Qi, Samsung Electronics R&D Institute UK at Cambridge Wireless event Radio technology for 5G – making it work
*** SHARED WITH PERMISSION ***
Ethernet OAM evolution



Ethernet OAM evolutionNir Cohen In this presentation, RAD’s Chief Scientist, Dr. Yaakov Stein, reviews the evolution of Ethernet OAM tools and practices and discusses the drivers for their developm
Ethernet OAM (fujitsu)



Ethernet OAM (fujitsu)Puran Pangeni 1) Ethernet Service OAM provides fault management and performance management capabilities for Ethernet services through standards developed by IEEE 802.1, ITU-T SG 13, and MEF.
2) It uses a multi-domain network model with customer, provider, and operator domains and defines functions like continuity check messages, loopback, and link trace to monitor services.
3) The standards define protocols for measuring performance metrics like frame loss ratio, frame delay, and frame delay variation between endpoints.
Ad
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Volte troubleshooting



Volte troubleshootingJamil Awan The document discusses VoLTE optimization services including RAN and EPC analysis using various tools. It details accomplishments like optimizing sites for carriers and analyzing problems like VoLTE drop issues. The key services described are VoLTE parameter audits, drive log analysis, UETR analysis, and end-to-end VoLTE call tracing. Case studies provided examine issues like QCI profile not defined, RRC drops without VoLTE drops, and improvements gained from features like ICIC and parameter changes.
LTE Interference troubleshooting guide



LTE Interference troubleshooting guideKlajdi Husi The document discusses fault analysis and troubleshooting of LTE antenna and feeder systems. It describes techniques like RSSI analysis, frequency scanning, interference detection tests, and DTP testing to identify issues like passive intermodulation (PIM) and determine if the fault is in the antenna tower or below. Parameters for simulated load testing and online interference monitoring are also outlined.
UMTS/LTE/EPC Call Flows for CSFB



UMTS/LTE/EPC Call Flows for CSFBJustin MA (馬嘉昌) It is a handbook of UMTS/LTE/EPC CSFB call flows.
This document is originally edited by Justin MA and it is free to share to everyone who are interested.
All reference/resource are from internet. If there is any copy-right issue, please kindly inform Justin by majachang@gmail.com.
Thanks for your reading!
LTE Call Processing and Handover



LTE Call Processing and HandoverSitha Sok •CPS (Call Processing Software): LTE Control & Bearer Protocol processing
•OAM (Operation and Maintenance): eNB Operation and Maintenance
•MW (Middleware): IPC and Redundancy function
•IPRS (IP Routing Software): Routing protocol operation
•NP SW (Network Processor Software): Packet forwarding function
•OS (Operating System): Embedded Linux
•DD (Device Driver): initializing and setting the devices
5G_NR_Overview_Architecture_and_Operating_Modes



5G_NR_Overview_Architecture_and_Operating_ModesAalekh Jain 5G/NR wireless communication technology overview, architecture and its operating modes SA and NSA. Also an introduction to VoNR and other services overview of 5G network.
The key technologies of 5G namely MIMO and Network slicing are also explained.
5g architecture, Industrial Training



5g architecture, Industrial TrainingSumanPramanik7 The document discusses the evolution of network architectures from 2G to 5G. It describes the key network elements and interfaces in 2G, 3G, 4G and 5G networks. The 5G network architecture uses both a reference point architecture for the user plane and a service-based architecture for the control plane. The main network functions in the 5G control plane are the AMF, SMF, UDM, AUSF, NSSF, NEF, NRF and UDR. The UPF is the main network element in the user plane.
LTE and EPC Specifications



LTE and EPC Specificationsaliirfan04 This document outlines the 3GPP specifications process for developing new mobile network systems and features. It follows a three stage process:
Stage 1 defines service requirements. Stage 2 defines the network architecture, elements, and high-level flows. Stage 3 defines protocols, state machines, and messages.
This process was applied to developing LTE, where Stage 1 documents defined requirements like throughput rates and latency. Stage 2 documents described the overall LTE system architecture. Numerous Stage 3 specifications then defined the protocols that enable LTE.
Advanced: 5G Service Based Architecture (SBA)



Advanced: 5G Service Based Architecture (SBA)3G4G A quick look at 5G System architecture in Reference point representation and in Service Based representation and also look at the different Network Functions (NFs) within the 5G System.
Ericsson RBS 6000



Ericsson RBS 6000ibrahimnabil17 The document summarizes the Ericsson RBS6000 series of radio base stations, which were popular in the last decade. It describes the modular design using different units like Digital Units and Radio Units to support configurations. It provides examples of configurations including racks and shelves. It also describes the evolution of the GSM modules from early DUG10/RUG designs to later DUG20/RUS designs with baseband processing. UMTS and LTE modules are also introduced. Combined GSM/UMTS/LTE configurations using modules like DUS31/41 are highlighted. Finally it discusses opportunities for Osmocom software to support these radios by adding E1/TDM user plane support.
Lte basic parameters



Lte basic parametersLinh Phạm LTE uses various frequency bands and duplexing techniques to provide high-speed data and peak download speeds of up to 300 Mbps. It supports mobility of up to 350 km/h and uses advanced technologies like OFDM, SC-FDMA, MIMO and turbo coding to achieve low latency and high bandwidth. LTE specifications define channel bandwidths of 1.4, 3, 5, 10, 15 and 20 MHz with modulation schemes of QPSK, 16QAM and 64QAM.
Lte signaling



Lte signalingMansour Naslcheraghi The document provides an overview of cellular communications signaling for LTE, LTE-A, and 4G technologies. It describes the LTE architecture including functions of the evolved node B, mobility management entity, serving gateway, home subscriber server, and PDN gateway. It also provides details on the LTE physical layer including OFDMA modulation, reference signal measurements for handover, and an example handover procedure using the X2 interface. In conclusion, it discusses key criteria for designing handovers and aspects for further research.
LTE: X2 interface



LTE: X2 interfaceSchwannden Kuo The document discusses the X2 interface and X2 handover procedure in LTE networks. The X2 interface connects two neighboring eNodeBs and establishes an X2 connection through the X2 setup procedure. The X2 handover procedure allows handing over a UE's connection from a source eNodeB to a target eNodeB, involving preparation where the target allocates resources and the UE connects to it, and execution including a path switch to route data to the target eNodeB. Key information like UE context and bearers is exchanged between eNodeBs through the X2 interface to enable smooth handover.
Radio Measurements in LTE



Radio Measurements in LTESofian . The document discusses various LTE measurement parameters and procedures including:
1. The eNB reports a list of detected PRACH preambles and measures timing advance, average RSSI, average SINR, UL CSI, and transport BLER for RRM purposes.
2. UE measurements include CQI, RSRP, and RSRQ while eNB measurements include timing advance, RSSI, SINR, UL CSI, detected preambles, and transport BLER. Inter-RAT measurements are also discussed.
3. Examples of RSRP, RSRQ, and timing advance procedures are provided along with CQI measurement details. PLMN selection, cell selection,
Tti bundling in fdd and tdd



Tti bundling in fdd and tddLaxman Mewari TTI bundling is a technique used in LTE to improve uplink coverage for voice calls by transmitting the same transport block containing voice data over multiple consecutive subframes without waiting for HARQ feedback. This provides a coding gain of up to 4dB compared to single subframe transmission, allowing power-limited UEs at the cell edge to be received with sufficient quality. TTI bundling can be implemented in both FDD and TDD LTE networks but with some differences due to limitations on consecutive uplink subframes in TDD configurations. It provides lower latency voice transmission compared to alternatives like RLC segmentation while reducing overhead.
LTE optimization



LTE optimizationجامعة تعز كلية الهندسة وتقنية المعلومات Taiz University Engineering This document describes the design of an LTE network optimization project by a group of students from Taiz University. It includes an introduction to LTE, the network planning process, and LTE system architecture. The network planning section discusses coverage planning including link budget calculations and propagation models, as well as capacity planning considering factors like interference levels and supported modulation schemes. The document also provides an overview of LTE system architecture components including the user equipment, E-UTRAN, EPC, and functions of each. It concludes with a section on LTE radio frequency optimization methods.
Lte default and dedicated bearer / VoLTE



Lte default and dedicated bearer / VoLTEmanish_sapra LTE uses EPS bearers to carry user data traffic. There are two types of EPS bearers - default bearers and dedicated bearers. Default bearers are created for each PDN connection and provide basic "best effort" internet access. Dedicated bearers provide additional tunnels for specific traffic like VoLTE and can have guaranteed bitrates. Dedicated bearers are linked to a default bearer and inherit properties like the PDN address from the default bearer. GTP is the protocol used to encapsulate and carry bearer traffic through the LTE core network.
How to dimension user traffic in LTE



How to dimension user traffic in LTEAlthaf Hussain The document discusses how to characterize and dimension user traffic in 4G networks. It describes how to define data traffic in terms of data speed and data tonnage. Data speed is the rate at which data is transferred, while data tonnage refers to the total amount of data exchanged. The document provides examples of data speed metrics used in 3GPP standards and outlines factors to consider when calculating expected data usage per subscriber based on typical mobile application usage patterns and available data plans. Dimensioning user traffic accurately is important for designing 4G networks to meet capacity demands.
Anr feature in lte



Anr feature in lteLokendra Rathore The document discusses Ericsson's Automatic Neighbor Relation (ANR) feature. It explains that ANR improves network performance and reduces maintenance by automatically detecting, adding, and setting up neighbor relations between cells. This allows seamless handovers and prevents dropped calls when sites go down. The document outlines how ANR works for intra-frequency, inter-frequency, and inter-RAT neighbor detection in LTE, UTRAN, and GERAN networks. It also describes ANR parameters, functions, and the affected network features.
LTE KPI



LTE KPISitha Sok 1) The document describes key performance indicators (KPIs) for measuring the performance of an LTE radio network. It defines KPIs related to accessibility, retainability, mobility, and latency.
2) Accessibility KPIs measure aspects like call setup success rate, RRC setup success rate, and E-RAB setup success rate. Mobility KPIs evaluate handover success rates within LTE and between LTE and other technologies.
3) Retainability KPIs track metrics such as call drop rate and call setup completion rate. The document also provides details on how to calculate each KPI and which counters are needed to measure the underlying events.
5G NR: Key features and enhancements



5G NR: Key features and enhancements3G4G An overview of 5G NR key technical features and enhancements for massive MIMO, mmWave, etc.
Presented by Yinan Qi, Samsung Electronics R&D Institute UK at Cambridge Wireless event Radio technology for 5G – making it work
*** SHARED WITH PERMISSION ***
Viewers also liked (20)
Ethernet OAM evolution



Ethernet OAM evolutionNir Cohen In this presentation, RAD’s Chief Scientist, Dr. Yaakov Stein, reviews the evolution of Ethernet OAM tools and practices and discusses the drivers for their developm
Ethernet OAM (fujitsu)



Ethernet OAM (fujitsu)Puran Pangeni 1) Ethernet Service OAM provides fault management and performance management capabilities for Ethernet services through standards developed by IEEE 802.1, ITU-T SG 13, and MEF.
2) It uses a multi-domain network model with customer, provider, and operator domains and defines functions like continuity check messages, loopback, and link trace to monitor services.
3) The standards define protocols for measuring performance metrics like frame loss ratio, frame delay, and frame delay variation between endpoints.
Leaky Bucket & Tocken Bucket - Traffic shaping



Leaky Bucket & Tocken Bucket - Traffic shapingVimal Dewangan This presentation provides a description about the traffic shaping in computer network like leaky bucket and token bucket and their differences
Megaplex nerc-cip-compliance



Megaplex nerc-cip-complianceNir Cohen NERC-CIP’s most recent release, version 5, focuses primarily on BES substations and their critical Cyber Assets (CA), by establishing an Electronic Security Perimeter (ESP) around the substation’s control system. RAD’s Megaplex, a major building block in RAD’s Service Assured Networking (SAN) solutions for power utilities, is strategically located to manage all electronic access to the substation and the cyber assets within it from external and internal attacks.
This paper reviews Megaplex’ 3-tier ESP protection and outlines how it helps power utilities boost their compliance with NERC CIP 005 and 007 requirements
23077 carrier ethernet-trends-challenges



23077 carrier ethernet-trends-challengesNir Cohen A review of current trends and challenges in the Carrier Ethernet services market, various deployment strategies adopted by service providers and their effects on network access planning
Power Utilities Migration Solutions



Power Utilities Migration SolutionsNir Cohen This document discusses power utility challenges in migrating from legacy telecommunications networks to next-generation packet networks. It outlines the need to replace obsolete equipment while maintaining interoperability with existing infrastructure. It also addresses challenges around terminating analog/leased line services and introducing new packet-based services. RAD solutions are presented as addressing these challenges through hybrid TDM/packet networks, carrier-grade Ethernet, and evolutionary migration paths to facilitate a smooth transition while ensuring network reliability, security and future scalability.
Assuring Superior VNF Performance at the Network Edge



Assuring Superior VNF Performance at the Network EdgeADVA At GEN15 we’re showcasing how communication service providers can integrate NFV-centric services with existing operational processes. This is a joint demonstration with Time Warner Cable Business Class and Juniper Networks.
harjeet singh 2nd



harjeet singh 2ndharjeet singh Harjeet Singh is seeking a position in a results-oriented organization where he can utilize his skills and education. He has over 2.5 years of experience in network operations and management with Ericsson and Nokia. He is proficient with transmission equipment from Ericsson, Huawei, and Nokia and network management systems including SOEM, SOM, and Huawei U2000. Harjeet holds a B.Tech in Electronics and Communication Engineering and has worked on network planning, optimization, and troubleshooting wireless networks.
SD-WAN 2.0: Building a Better SD-WAN, October 2016



SD-WAN 2.0: Building a Better SD-WAN, October 2016ADVA Prayson Pate's presentation at SDN World Congress outlined how virtualization can take SD-WAN to the next stage.
Leaky bucket A



Leaky bucket ASyed Shaheer Gilani The document discusses the leaky bucket algorithm for traffic shaping. It begins with an introduction to congestion and traffic shaping. It then provides an overview of the leaky bucket algorithm, describing it as a method that converts bursty traffic into fixed-rate traffic by allowing packets to accumulate in a virtual "leaky bucket" at a set rate before entering the network. The document includes an example demonstrating how the algorithm works with different sized packets in a queue. It discusses parameters like burst rate and average rate and describes uses of the algorithm in networks including shaping bursty traffic to a sustained cell flow rate.
ZTE COMMUNICATIONS No.2 2016 : Optical wireless communications



ZTE COMMUNICATIONS No.2 2016 : Optical wireless communicationsSitha Sok ZTE COMMUNICATIONS No.2 2016
Fresh off the Press! The April issue focuses on optical wireless communications. Harald Hass, "the father of Li-Fi", and his student contributed to this special issue.
Quality of Service at the Internet Engineering Task Force



Quality of Service at the Internet Engineering Task ForceJohn Loughney "Quality of Service at the Internet Engineering Task Force" Workshop on "End-to-End Quality of Service. What is it? How do we get it?" Geneva, 1-3 October 2003.
ZTE TECHNOLOGIES No.3 2016 - Special topic: Big Video



ZTE TECHNOLOGIES No.3 2016 - Special topic: Big VideoSitha Sok Special Topic
- The Road to Big Video Revolution
- PSVN: The Ultimate Path to Video Transmission Network
- Big Video Best View
- Promising CDN in the Big Video Era
Fso free space optic 



Fso free space optic Abel Ngetich This document discusses Free Space Optic (FSO) technology, which uses lasers and photodetectors to transmit data, voice, or video at speeds up to 2.5 Gbps in an optical connection without the need for fiber. FSO consists of an optical transceiver with a laser transmitter and photodetector receiver to provide bidirectional communication using invisible infrared laser light. While FSO has advantages like huge bandwidth and low interference, it also has disadvantages such as needing line of sight and being susceptible to signal scattering. The cost of installing FSO units on a campus is estimated to be $4,600-$26,840 per connection depending on indoor or outdoor installation requirements.
Microwave backhaul gets a boost with multiband



Microwave backhaul gets a boost with multibandSitha Sok Is there a spectrum shortage? The answer to the question is both yes and no; in some locations spectrum is severely congested, while in other places it is highly underutilized
Emerging Technologies of Future Multimedia Coding, Analysis and Transmission



Emerging Technologies of Future Multimedia Coding, Analysis and TransmissionSitha Sok Emerging Technologies of Future Multimedia Coding, Analysis and Transmission.
Overview of the Second Generation AVS Video Coding Standard (AVS2).
An Introduction to High Efficiency Video Coding Range Extensions.
Multi⁃Layer Extension of the High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC) Standard
Broadband Cellular Communication (Vol 2 Issue 2)



Broadband Cellular Communication (Vol 2 Issue 2)JournalsPub www.journalspub.com This paper proposes two new algorithms, Gaussian RED (G-RED) and modified Gaussian RED (MG-RED), to improve congestion control in mobile ad hoc networks (MANETs) compared to the traditional RED algorithm. G-RED and MG-RED use Gaussian and modified Gaussian functions respectively in the RED algorithm to determine when to drop packets. The paper presents that G-RED and MG-RED outperform traditional RED in terms of throughput, packet delivery fraction, and number of packets dropped by better managing the network queue.
Fso



FsoShiva Krishna Chandra Shekar This document discusses free space optics (FSO) technology, which uses lasers to transmit data through the air instead of fiber optic cables. It provides details on how FSO systems work and their advantages over fiber, including significantly lower costs and faster deployment times. However, it also notes challenges like signal attenuation from weather conditions like heavy rain or fog. The document examines applications of FSO including extending metro networks and enterprise campus connectivity as well as potential issues like beam misalignment from building sway.
Ad
Similar to What is-twamp (20)
Deploying Carrier Ethernet 2.0 services based on Raisecom technology.pdf



Deploying Carrier Ethernet 2.0 services based on Raisecom technology.pdfnimaw11254 Indice
• CE 1.0 vs CE 2.0
• Servicios CE 2.0
• Soluciones Raisecom CE 2.0
• Agregación y Acceso
• Escenarios de Aplicación
• MEF attributes
• Reliability
• Service management
• QoS
• Scalability
• Más allá de CE 2.0 – Service activation ITU-T Y.1564
Hardened Ethernet In ITS 2010



Hardened Ethernet In ITS 2010ethersteve This document summarizes a presentation given by Steve Frank of EtherWAN, a manufacturer of Ethernet networking devices. EtherWAN focuses on producing environmentally hardened Ethernet switches and media converters for applications in transportation infrastructure, security/surveillance, and smart grid utilities. Their devices are designed to operate in extreme temperatures and withstand vibration. EtherWAN provides managed and unmanaged switches with features like VLAN tagging, QoS, port security, and fast recovery from link failures. Their hardened devices are suited for network edge applications requiring reliability.
PLNOG 13: Piotr Głaska: Quality of service monitoring in IP networks



PLNOG 13: Piotr Głaska: Quality of service monitoring in IP networksPROIDEA Piotr Głaska – Senior Product Manager at Huawei, Enterprise Networking department. Experienced in management, design and deployment of IP solutions, for 17 years worked for various companies as service provides, through the end-user, integrator, up to device producer. The Huawei Certified Datacom Proffesional HCDP, Cisco CCIE #15966 and HP MASE.
Topic of Presentation: Quality of service monitoring in IP networks
Language: Polish
Abstract: TBD
Veryx Product Catalog - ATTEST



Veryx Product Catalog - ATTESTVeryx Technologies Veryx ATTEST range of testing solutions enable NEMs and NSPs reduce the time taken to test with automated test suites in an integrated testing framework providing many tester-friendly features such as flexible DUT control, GUI or CLI-based access, easy debugging and detailed reporting.
Accelerating lte-a-deployments



Accelerating lte-a-deploymentsNir Cohen This document discusses innovative approaches from RAD for accelerating LTE/LTE-A deployment and improving performance monitoring. It introduces RAD's distributed IEEE 1588 Grandmaster, which is built into an SFP module and can turn any network equipment into a precision timing source. This eliminates the need for expensive upgrades. RAD also presents its MiNID solution, which is a miniature programmable network interface device in an SFP sleeve that allows any device to monitor performance across LTE backhaul networks.
PLNOG 17 - Marek Janik - Sieć dla IXP



PLNOG 17 - Marek Janik - Sieć dla IXPPROIDEA W trakcie sesji przedstawione zostaną różne sposoby budowania rozproszonych punktów wymiany ruchu internetowego. Zaprezentowane zostanie również jak w praktyce wykorzystano protokół TRILL w Slovak Internet Exchange.
SDI to IP 2110 Transition Part 2



SDI to IP 2110 Transition Part 2Dr. Mohieddin Moradi The document outlines topics related to video over IP infrastructure and standards. It discusses IP technology trends, networking basics, video and audio over IP standards, SMPTE ST 2110, NMOS, infrastructure considerations, timing issues, clean switching methods, compression, broadcast controller/orchestration, and case studies for migrating broadcast facilities to IP. The document provides an overview and outline for presenting on designing, integrating, and managing IP-based broadcast facilities and production workflows.
Enabling Active Flow Manipulation (AFM) in Silicon-based Network Forwarding E...

Enabling Active Flow Manipulation (AFM) in Silicon-based Network Forwarding E...Tal Lavian Ph.D. Programmable Internet:
Enhance internetworking functions.
Move computations into the network for value added services.
Manage the network more capably than possible with SNMP.
More quickly introduce Diffserv or Inserv to support new multimedia applications
Implement traffic control algorithms to support QoS.
S5850 datasheet



S5850 datasheetTeresa Huang The Fiberstore FS S5850 Series Routing Switches are high performance Ethernet switches to meet next generation Metro, Data Center and Enterprise network requirements.
S5850 datasheet



S5850 datasheetTeresa Huang The Fiberstore FS S5850 Series Routing Switches are high performance Ethernet switches
to meet next generation Metro, Data Center and Enterprise network requirements. FS
S5850 is designed based on the fourth generation high-end scalable chipset , which support L2/L3/Data Center/Metro features.
S5850 3-datasheet



S5850 3-datasheetTeresa Huang The Fiberstore FS S5850 Series Routing Switches are high performance Ethernet switches to meet next generation Metro, Data Center and Enterprise network requirements. FS S5850 is designed based on the fourth generation high-end scalable chipset , which support L2/L3/Data Center/Metro features. The FS S5850 comes with complete system software with comprehensive protocols and applications to facilitate rapid service deployment and management for both traditional L2/L3 networks and Data Center networks.
S5850 3-datasheet



S5850 3-datasheetTeresa Huang The Fiberstore FS S5850 Series Routing Switches are high performance Ethernet switches to meet next generation Metro, Data Center and Enterprise network requirements. FS S5850 is designed based on the fourth generation high-end scalable chipset , which support L2/L3/Data Center/Metro features. The FS S5850 comes with complete system software with comprehensive protocols and applications to facilitate rapid service deployment and management for both traditional L2/L3 networks and Data Center networks.
S5850 datasheet



S5850 datasheetTeresa Huang The FS S5850 Series are cost-effective Ethernet access and aggregation platform to Enterprise, Data Center and Metro application. The FS S5850 Series Switches currently includes four configurations: S5850-48S2Q4C/S5850-48S6Q/FS S5850 and S5850-32S2Q.
S5850 3-datasheet



S5850 3-datasheetTeresa Huang The Fiberstore FS S5850 Series Routing Switches are high performance Ethernet switches to meet next generation Metro, Data Center and Enterprise network requirements. FS S5850 is designed based on the fourth generation high-end scalable chipset , which support L2/L3/Data Center/Metro features. The FS S5850 comes with complete system software with comprehensive protocols and applications to facilitate rapid service deployment and management for both traditional L2/L3 networks and Data Center networks.
WGS-5225-8T2SV Industrial Wall-mount Managed Switch with LCD Touch Screen



WGS-5225-8T2SV Industrial Wall-mount Managed Switch with LCD Touch ScreenBluBoxx Communication Pvt. ltd WGS-5225-8T2SV, an innovative, Industrial 8-port 10/100/1000T + 2-port 100/1000/2500BASE-X SFP Wall-mount Managed Switch with LCD Touch Screen, offers IPv6/IPv4 dual stack management, intelligent Layer 2 and Layer 4 management functions, and user-friendly interface. The WGS-5225-8T2SV is able to operate reliably, stably and quietly in any environment without affecting its performance. Featuring ultra networking speed and operating temperature ranging from -20 to 70 degrees C in a compact but rugged IP30 metal housing, the WGS-5225-8T2SV is an ideal solution to meet the demand for the following network applications:
■ Building/Home automation network
■ Internet of things (IoT)
■ IP surveillance
■ Wireless LAN
RNEC N101 Lite- RAX711-L.pptx



RNEC N101 Lite- RAX711-L.pptxJean Carlos Cruz This document provides an overview of a 4-day training course on Carrier Ethernet. Day 1 covers introductions, product overviews, and carrier Ethernet services. Day 2 covers device security, switchport configurations, and QoS. Day 3 focuses on Ethernet CFM and service activation tests. Day 4 covers scenario-based exercises and SNMP monitoring. The training aims to provide attendees with knowledge and hands-on experience in deploying and managing Carrier Ethernet networks and services.
Enterprise network design multi layer network and security.pptx



Enterprise network design multi layer network and security.pptxbipinbhattarai12 a must read for design and analysis
IGS-5225-4T2S Industrial Managed Ethernet Switch



IGS-5225-4T2S Industrial Managed Ethernet SwitchBluBoxx Communication Pvt. ltd IGS-5225-4T2S, the smallest, fully-managed Gigabit fiber switch for harsh environments, features 4 10/100/1000Mbps copper ports, 2 100/1000X SFP ports and redundant power system in an IP30 rugged but compact-sized case. The IGS-5225-4T2S can be installed in any difficult environment as it can operate stably under the temperature range from -40 to 75 degrees C. With such a slim enclosure, it does not need a big space to install.
The switch features user-friendly yet advanced IPv6/IPv4 management interfaces, abundant L2/L4 switching functions and Layer 3 static routing capability. It allows either DIN-rail or wall mounting for efficient use of cabinet space. With 2 dual-speed SFP fiber slots, it can be flexibly applied to extend the connection distance.
Contact us
Tel: +91-7875432180 Email: sales@bbcpl.in
Website: https://www.bbcpl.in
Enhancing Network Visibility Based On Open Converged Network Appliance



Enhancing Network Visibility Based On Open Converged Network ApplianceOpen Networking Summit Dr. Dongheon Lee' and Dr. Junho Suh's presentation from the 2017 Open Networking Summit.
As the mobile traffic carried by cellular networks has been growing rapidly and the networks gets bigger and more complex, network operators have been forced to search for solutions to substantially enhance network visibility. This talk introduces SKT integrated Network Analyzer (TiNA) and Converged Appliance Platform (T-CAP) which help us improving the efficiency of network operation, troubleshooting, and analyzing traffic. TiNA is composed of virtual network packet broker, flow analyzer, high speed packet dump system, connection performance analyzer, and 3D-based network management system. T-CAP is an open architecture of a server-switch type hardware. We will review how to implement those TiNA functions based on open source (e.g., DPDK, Spark Streaming) and T-CAP. Finally, we will also discuss about the use-cases of TiNA and T-CAP for the private cloud & telco network infrastructure.
Performance Evaluation of GTP-U and SRv6 Stateless Translation



Performance Evaluation of GTP-U and SRv6 Stateless TranslationChunghan Lee The GPRS Tunneling Protocol User Plane (GTP-U) has long been deployed for GSM, UMTS and 4G LTE. Now for 5G, IPv6 Segment Routing (SRv6) has been proposed as an alternative user plane protocol to GTP-U in both 3GPP and IETF. SRv6 based on source routing has many advantages: stateless traffic steering, network programming and so on. Despite the advantages, it is hard to expect to replace GTP-U by SRv6 all at once, even in a 5G deployment because of a lot of dependencies between 3GPP nodes. Therefore, stateless translation and co- existence with GTP-U have been proposed in IETF. However there are no suitable measurement platform and performance evaluation results between GTP-U and SRv6. In particular, it is hard to measure latency on commercial traffic generators when a receiving packet type is different from a sending packet type. In this paper, we focus on the performance evaluation between GTP-U and SRv6 stateless translation. We designed an SRv6 measurement platform using a programmable switch, and measured GTP-U and SRv6 functions with pre-defined scenarios on a local environment. Well-known performance metrics, such as throughput and packets per second (PPS), are measured by the traffic generator while the latency at the functions was measured using telemetry on our SRv6 platform. In our evaluation, we cannot find the abrupt performance drop of well-known metrics at SRv6 stateless translation. Moreover, the latency of SRv6 stateless translation is similar to GTP-U and their performance degradation is negligible. Through the evaluation results, it is obvious that the SRv6 stateless translation is acceptable to the 5G user plane.
WGS-5225-8T2SV Industrial Wall-mount Managed Switch with LCD Touch Screen



WGS-5225-8T2SV Industrial Wall-mount Managed Switch with LCD Touch ScreenBluBoxx Communication Pvt. ltd
Ad
More from Nir Cohen (14)
Robust Cyber Security for Power Utilities



Robust Cyber Security for Power UtilitiesNir Cohen The security of critical networks is at the center of attention of industry and government regulators alike. Check Point and RAD offer a joint end-to-end cyber security solution that protects any utility operational technology (OT) network by eliminating RTU and SCADA equipment vulnerabilities, as well as defends against cyber-attacks on the network’s control and data planes. This solution brief explains how the joint solution enables compliance with NERC-CIP directives, provides deep visibility and control of ICS/SCADA communications, and allows secure remote access into OT networks.
V cpe deployment-best-practices-presentation



V cpe deployment-best-practices-presentationNir Cohen A review of the various vCPE implementation options available for service providers and the factors that should be considered to avoid pitfalls and ensure optimal results.
Distributed NFV: Ensuring that the Benefits of Virtualization Exceed the Costs



Distributed NFV: Ensuring that the Benefits of Virtualization Exceed the CostsNir Cohen Dr. Yuri Gittik is taking a closer look at the different approaches to implement NFV solutions is carrier networks, the advantages and disadvantages of each approach and how these approaches are affecting the implementation costs.
Carrier ethernet vs-mpls-power-utility-communications



Carrier ethernet vs-mpls-power-utility-communicationsNir Cohen As SDH/SONET networks are being phased out, power utilities are starting to migrate to future-proof packet networks. This presentation reviews and compares Carrier Ethernet, MPLS and MPLS-TP to help power utilities determine which alternative offers the best fit for the operational needs of their mission-critical applications.
Time distribution strategies in cellular networks



Time distribution strategies in cellular networksNir Cohen This paper reviews the various methodologies currently available for ensuring Time of Day (ToD) synchronization in cellular networks. It also introduces RAD’s revolutionary Distributed GMTM scheme, designed to deliver superb ToD accuracy at a lower cost in LTE and small cell networks, by bringing Grandmaster functionality closer to the base station in a small form factor device.
Mobile backhaul solution guide



Mobile backhaul solution guideNir Cohen This paper presents a brief overview of today’s mobile backhaul market, outlines the unique challenges facing mobile operators and backhaul transport providers, and suggests strategies for improving network performance and coverage. Key emphasis is on the OAM, resiliency, Quality of Service (QoS) and timing technologies required for cost-efficient backhaul of 2G/3G/4G/LTE and small cells traffic.
Carrier ethernet-for-power-utilities-presentation



Carrier ethernet-for-power-utilities-presentationNir Cohen This document discusses how carrier-grade Ethernet can ensure reliable communications for utility networks transitioning to support smart grid applications. It covers Ethernet mechanisms that provide carrier-grade performance such as quality of service, resiliency, monitoring and timing synchronization. Choosing between IP, MPLS and Ethernet options is discussed. The document also addresses network security considerations and introduces RAD's carrier-grade Ethernet product portfolio for power utilities.
Carrier grade ethernet for power utilities - solution paper



Carrier grade ethernet for power utilities - solution paperNir Cohen This paper reviews the various tools that carrier-grade Ethernet offers to meet the performance required from the ICT network and discusses strategies for the transition to Smart Grid communications
Ethernet vs-mpls-tp-in-the-access-presentation



Ethernet vs-mpls-tp-in-the-access-presentationNir Cohen A presentation given by RAD’s CTO, Dr. Yaakov Stein, at the 2012 MPLS and Ethernet World Congress. The presentation compares the two technologies in ten critical categories and grades them on suitability, coverage and maturity
Timing over packet demarcation



Timing over packet demarcationNir Cohen There is a pressing need to distribute accurate timing, i.e., frequency and/or Time of Day (ToD), across Packet Switched Networks (PSNs) for applications such as cellular backhaul. This paper reviews the main issues involved in timing over packet (ToP) demarcation and provides best practices for ToP demarcation and performance monitoring.
Teleprotection over packet f 30 8-11



Teleprotection over packet f 30 8-11Nir Cohen Teleprotection signals from protective relays are among the most critical data transmitted across utility networks, as they help manage the power grid load, as well as to protect equipment within the power network from severe damages resulting from faulty HV lines. By enabling load-sharing, grid adjustments and immediate fault clearance, Teleprotection has a decisive role in ensuring uninterrupted power supply and therefore requires special attention with regards to network performance and reliability. Specifically, protection commands must be assured immediate delivery when problems are detected, so that faulty equipment can be disconnected before causing a system-wide damage.
Ce the cio perspective part iii v2 1 9-6-11



Ce the cio perspective part iii v2 1 9-6-11Nir Cohen This is the third presentation out of 3 on Slideshare reviewing the enterprise needs, issues and considerations from WAN services from CIO point of view. This presentation series is for CIOs and the providers that offer such services. All you need to know about carrier Ethernet service levels and SLAs – what matters to the users and what a service provider should offer.
Part I – why chose carrier Ethernet WAN services
Part II – Service levels and SLA
Part III – Ethernet and IP VPNs – when to use each
Ce the cio perspective part ii v2 3 21-6-11



Ce the cio perspective part ii v2 3 21-6-11Nir Cohen This is the second presentation out of 3 on Slideshare reviewing the enterprise needs, issues and considerations from WAN services from CIO point of view. This presentation series is for CIOs and the providers that offer such services. All you need to know about carrier Ethernet service levels and SLAs – what matters to the users and what a service provider should offer.
Part I – why chose carrier Ethernet WAN services
Part II – Service levels and SLA
Part III – Ethernet and IP VPNs – when to use each
Ce the cio perspective part ii v2 3 21-6-11



Ce the cio perspective part ii v2 3 21-6-11Nir Cohen Carrier Ethernet SLAs typically include commitments for bandwidth, class of service levels, quality of service guarantees, and response times. Key performance indicators covered include availability, latency, jitter, and packet loss, which can affect user experience. Monitoring and reporting tools are important to ensure the provider is meeting the guaranteed SLA levels. Service providers implement traffic management, monitoring, fault detection and repair tools to guarantee Carrier Ethernet SLAs.
Recently uploaded (20)
Mastering Testing in the Modern F&B Landscape



Mastering Testing in the Modern F&B Landscapemarketing943205 Dive into our presentation to explore the unique software testing challenges the Food and Beverage sector faces today. We’ll walk you through essential best practices for quality assurance and show you exactly how Qyrus, with our intelligent testing platform and innovative AlVerse, provides tailored solutions to help your F&B business master these challenges. Discover how you can ensure quality and innovate with confidence in this exciting digital era.
Risk Analysis 101: Using a Risk Analyst to Fortify Your IT Strategy



Risk Analysis 101: Using a Risk Analyst to Fortify Your IT Strategyjohn823664 Discover how a minor IT glitch became the catalyst for a major strategic shift. In this real-world story, follow Emma, a CTO at a fast-growing managed service provider, as she faces a critical data backup failure—and turns to a risk analyst from remoting.work to transform chaos into clarity.
This presentation breaks down the essentials of IT risk analysis and shows how SMBs can proactively manage cyber threats, regulatory gaps, and infrastructure vulnerabilities. Learn what a remote risk analyst really does, why structured risk management matters, and how remoting.work delivers vetted experts without the overhead of full-time hires.
Perfect for CTOs, IT managers, and business owners ready to future-proof their IT strategy.
👉 Visit remoting.work to schedule your free risk assessment today.
How Top Companies Benefit from Outsourcing



How Top Companies Benefit from OutsourcingNascenture Explore how leading companies leverage outsourcing to streamline operations, cut costs, and stay ahead in innovation. By tapping into specialized talent and focusing on core strengths, top brands achieve scalability, efficiency, and faster product delivery through strategic outsourcing partnerships.
Building Connected Agents: An Overview of Google's ADK and A2A Protocol



Building Connected Agents: An Overview of Google's ADK and A2A ProtocolSuresh Peiris Google's Agent Development Kit (ADK) provides a framework for building AI agents, including complex multi-agent systems. It offers tools for development, deployment, and orchestration.
Complementing this, the Agent2Agent (A2A) protocol is an open standard by Google that enables these AI agents, even if from different developers or frameworks, to communicate and collaborate effectively. A2A allows agents to discover each other's capabilities and work together on tasks.
In essence, ADK helps create the agents, and A2A provides the common language for these connected agents to interact and form more powerful, interoperable AI solutions.
Multi-Agent AI Systems: Architectures & Communication (MCP and A2A)



Multi-Agent AI Systems: Architectures & Communication (MCP and A2A)HusseinMalikMammadli Multi-Agent AI Systems: Architectures & Communication (MCP and A2A)
React Native for Business Solutions: Building Scalable Apps for Success



React Native for Business Solutions: Building Scalable Apps for SuccessAmelia Swank See how we used React Native to build a scalable mobile app from concept to production. Learn about the benefits of React Native development.
for more info : https://www.atoallinks.com/2025/react-native-developers-turned-concept-into-scalable-solution/
UiPath AgentHack - Build the AI agents of tomorrow_Enablement 1.pptx



UiPath AgentHack - Build the AI agents of tomorrow_Enablement 1.pptxanabulhac Join our first UiPath AgentHack enablement session with the UiPath team to learn more about the upcoming AgentHack! Explore some of the things you'll want to think about as you prepare your entry. Ask your questions.
Top 5 Qualities to Look for in Salesforce Partners in 2025



Top 5 Qualities to Look for in Salesforce Partners in 2025Damco Salesforce Services 🔍 Top 5 Qualities to Look for in Salesforce Partners in 2025
Choosing the right Salesforce partner is critical to ensuring a successful CRM transformation in 2025.
Understanding SEO in the Age of AI.pdf



Understanding SEO in the Age of AI.pdfFulcrum Concepts, LLC This presentation dives into how artificial intelligence has reshaped Google's search results, significantly altering effective SEO strategies. Audiences will discover practical steps to adapt to these critical changes.
https://www.fulcrumconcepts.com/ai-killed-the-seo-star-2025-version/
Building a research repository that works by Clare Cady



Building a research repository that works by Clare CadyUXPA Boston Are you constantly answering, "Hey, have we done any research on...?" It’s a familiar question for UX professionals and researchers, and the answer often involves sifting through years of archives or risking lost insights due to team turnover.
Join a deep dive into building a UX research repository that not only stores your data but makes it accessible, actionable, and sustainable. Learn how our UX research team tackled years of disparate data by leveraging an AI tool to create a centralized, searchable repository that serves the entire organization.
This session will guide you through tool selection, safeguarding intellectual property, training AI models to deliver accurate and actionable results, and empowering your team to confidently use this tool. Are you ready to transform your UX research process? Attend this session and take the first step toward developing a UX repository that empowers your team and strengthens design outcomes across your organization.
Longitudinal Benchmark: A Real-World UX Case Study in Onboarding by Linda Bor...



Longitudinal Benchmark: A Real-World UX Case Study in Onboarding by Linda Bor...UXPA Boston This is a case study of a three-part longitudinal research study with 100 prospects to understand their onboarding experiences. In part one, we performed a heuristic evaluation of the websites and the getting started experiences of our product and six competitors. In part two, prospective customers evaluated the website of our product and one other competitor (best performer from part one), chose one product they were most interested in trying, and explained why. After selecting the one they were most interested in, we asked them to create an account to understand their first impressions. In part three, we invited the same prospective customers back a week later for a follow-up session with their chosen product. They performed a series of tasks while sharing feedback throughout the process. We collected both quantitative and qualitative data to make actionable recommendations for marketing, product development, and engineering, highlighting the value of user-centered research in driving product and service improvements.
Crazy Incentives and How They Kill Security. How Do You Turn the Wheel?



Crazy Incentives and How They Kill Security. How Do You Turn the Wheel?Christian Folini Everybody is driven by incentives. Good incentives persuade us to do the right thing and patch our servers. Bad incentives make us eat unhealthy food and follow stupid security practices.
There is a huge resource problem in IT, especially in the IT security industry. Therefore, you would expect people to pay attention to the existing incentives and the ones they create with their budget allocation, their awareness training, their security reports, etc.
But reality paints a different picture: Bad incentives all around! We see insane security practices eating valuable time and online training annoying corporate users.
But it's even worse. I've come across incentives that lure companies into creating bad products, and I've seen companies create products that incentivize their customers to waste their time.
It takes people like you and me to say "NO" and stand up for real security!
Google DeepMind’s New AI Coding Agent AlphaEvolve.pdf



Google DeepMind’s New AI Coding Agent AlphaEvolve.pdfderrickjswork In a landmark announcement, Google DeepMind has launched AlphaEvolve, a next-generation autonomous AI coding agent that pushes the boundaries of what artificial intelligence can achieve in software development. Drawing upon its legacy of AI breakthroughs like AlphaGo, AlphaFold and AlphaZero, DeepMind has introduced a system designed to revolutionize the entire programming lifecycle from code creation and debugging to performance optimization and deployment.
ICDCC 2025: Securing Agentic AI - Eryk Budi Pratama.pdf



ICDCC 2025: Securing Agentic AI - Eryk Budi Pratama.pdfEryk Budi Pratama Title: Securing Agentic AI: Infrastructure Strategies for the Brains Behind the Bots
As AI systems evolve toward greater autonomy, the emergence of Agentic AI—AI that can reason, plan, recall, and interact with external tools—presents both transformative potential and critical security risks.
This presentation explores:
> What Agentic AI is and how it operates (perceives → reasons → acts)
> Real-world enterprise use cases: enterprise co-pilots, DevOps automation, multi-agent orchestration, and decision-making support
> Key risks based on the OWASP Agentic AI Threat Model, including memory poisoning, tool misuse, privilege compromise, cascading hallucinations, and rogue agents
> Infrastructure challenges unique to Agentic AI: unbounded tool access, AI identity spoofing, untraceable decision logic, persistent memory surfaces, and human-in-the-loop fatigue
> Reference architectures for single-agent and multi-agent systems
> Mitigation strategies aligned with the OWASP Agentic AI Security Playbooks, covering: reasoning traceability, memory protection, secure tool execution, RBAC, HITL protection, and multi-agent trust enforcement
> Future-proofing infrastructure with observability, agent isolation, Zero Trust, and agent-specific threat modeling in the SDLC
> Call to action: enforce memory hygiene, integrate red teaming, apply Zero Trust principles, and proactively govern AI behavior
Presented at the Indonesia Cloud & Datacenter Convention (IDCDC) 2025, this session offers actionable guidance for building secure and trustworthy infrastructure to support the next generation of autonomous, tool-using AI agents.
UX for Data Engineers and Analysts-Designing User-Friendly Dashboards for Non...



UX for Data Engineers and Analysts-Designing User-Friendly Dashboards for Non...UXPA Boston Data dashboards are powerful tools for decision-making, but for non-technical users—such as doctors, administrators, and executives—they can often be overwhelming. A well-designed dashboard should simplify complex data, highlight key insights, and support informed decision-making without requiring advanced analytics skills.
This session will explore the principles of user-friendly dashboard design, focusing on:
-Simplifying complex data for clarity
-Using effective data visualization techniques
-Designing for accessibility and usability
-Leveraging AI for automated insights
-Real-world case studies
By the end of this session, attendees will learn how to create dashboards that empower users, reduce cognitive overload, and drive better decisions.
In-App Guidance_ Save Enterprises Millions in Training & IT Costs.pptx



In-App Guidance_ Save Enterprises Millions in Training & IT Costs.pptxaptyai Discover how in-app guidance empowers employees, streamlines onboarding, and reduces IT support needs-helping enterprises save millions on training and support costs while boosting productivity.
AI and Gender: Decoding the Sociological Impact



AI and Gender: Decoding the Sociological ImpactSaikatBasu37 Exploring the Intersection of Technology and Society. How does AI shape our understanding of gender, and what does it mean for society?
AI needs Hybrid Cloud - TEC conference 2025.pptx



AI needs Hybrid Cloud - TEC conference 2025.pptxShikha Srivastava Engaging interactive session at the Carolina TEC Conference—had a great time presenting the intersection of AI and hybrid cloud, and discussing the exciting momentum the #HashiCorp acquisition brings to #IBM."
What is-twamp
- 1. TWAMP Explained Measuring Performance in IP Networks September 2014
- 2. TWAMP Explained 2 What is TWAMP • Two-Way Active Measurement Protocol (IETF RFC 5357) • Uses active probe packets to measure two-way delay between two end-points in IP networks – Timestamps are applied for high accuracy • Typically does not requires that both end-points are time-synchronized – One-way delay measurements require sync. • Additional capabilities: packet loss ratio, continuity check, one-way and two-way packet delay variation
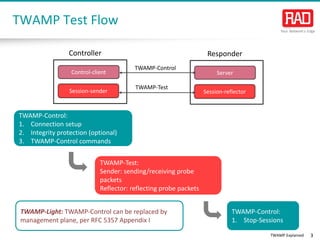
- 3. TWAMP Explained 3 TWAMP Test Flow TWAMP-Control: 1. Connection setup 2. Integrity protection (optional) 3. TWAMP-Control commands TWAMP-Test: Sender: sending/receiving probe packets Reflector: reflecting probe packets TWAMP-Control: 1. Stop-Sessions Server Session-reflector Control-client Session-sender TWAMP-Control TWAMP-Test Controller Responder TWAMP-Light: TWAMP-Control can be replaced by management plane, per RFC 5357 Appendix IT-Control
- 4. TWAMP Explained 4 TWAMP is mostly suitable for premium L3 business services (with SLA guarantees) and for LTE backhaul service assurance! • ICMP Echo (“Ping”): Internet Control Message Protocol (IETF RFC 792). Used for connectivity check and rough roundtrip delay estimations between any IP devices • IP SLA: Proprietary Cisco method for measuring performance across router networks Other L3 PM Methods
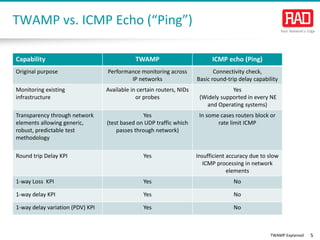
- 5. TWAMP Explained 5 Capability TWAMP ICMP echo (Ping) Original purpose Performance monitoring across IP networks Connectivity check, Basic round-trip delay capability Monitoring existing infrastructure Available in certain routers, NIDs or probes Yes (Widely supported in every NE and Operating systems) Transparency through network elements allowing generic, robust, predictable test methodology Yes (test based on UDP traffic which passes through network) In some cases routers block or rate limit ICMP Round trip Delay KPI Yes Insufficient accuracy due to slow ICMP processing in network elements 1-way Loss KPI Yes No 1-way delay KPI Yes No 1-way delay variation (PDV) KPI Yes No TWAMP vs. ICMP Echo (“Ping”)
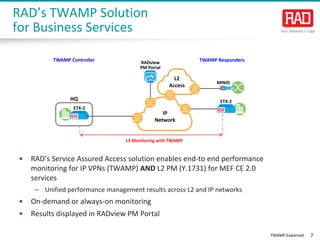
- 7. TWAMP Explained 7 • RAD’s Service Assured Access solution enables end-to end performance monitoring for IP VPNs (TWAMP) AND L2 PM (Y.1731) for MEF CE 2.0 services – Unified performance management results across L2 and IP networks • On-demand or always-on monitoring • Results displayed in RADview PM Portal RAD’s TWAMP Solution for Business Services IP Network L2 Access L3 Monitoring with TWAMP RADview PM Portal ETX-2 MiNID HQ ETX-2 TWAMP RespondersTWAMP Controller
- 8. TWAMP Explained 8 • Tight control of mobile backhaul transport networks for SLA assurance to meet stringent performance requirements in a dynamic LTE environment • On-demand or always-on monitoring, with presentation in RADview PM Portal RAD’s TWAMP Solution for LTE Backhaul IP Network/ Backhaul L2 Access L3 Monitoring with TWAMP RADview PM Portal Controller Site GbE/ 10 GbE ETX-2 MiNID ETX-2 TWAMP Responders TWAMP Controllers
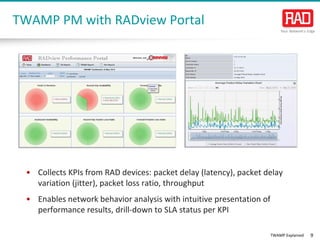
- 9. TWAMP Explained 9 • Collects KPIs from RAD devices: packet delay (latency), packet delay variation (jitter), packet loss ratio, throughput • Enables network behavior analysis with intuitive presentation of performance results, drill-down to SLA status per KPI TWAMP PM with RADview Portal
- 10. TWAMP Explained 10 • TWAMP is an effective standard-based method for monitoring performance in IP networks • Performance guarantees in L3 are now expected for premium business services and LTE backhaul • TWAMP support is therefore a critical element in the PM toolbox of service assurance NIDs • RAD’s Service Assured Access solution provides full L2 and L3 support for service delivery and performance monitoring in all form-factors: TWAMP Takeaways ETX-2 IP and Carrier Ethernet Demarcation MiNID Miniature Programmable NID RADview Performance Monitoring Portal V i s i t w w w . r a d . c o m f o r m o r e i n f o r m a t i o n
- 11. w w w . r a d . c o m

![[Tripo] 輕鬆架站使用 twamp](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/tripo-twamp-120830040759-phpapp02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)


